Like many other people, I’ve been trying to make sense of the horrific attack in Nice on 14 July. I’ve delayed writing about it because so much remains unknown – though that has not stopped a cascade of malignant certainties spewing from those on the Right who see every event as an opportunity to foment fear, harness hatred and deepen division.
A Tunisian man with no known history of political activism or religious affirmation kills 84 people by deliberately driving a truck through crowds along the Promenade des Anglais who were celebrating Bastille Day; a man who lived on the margins with a record of petty crime and domestic abuse; somebody with precious few resources, yet able to rent a truck and acquire weapons; and a claim to have ‘inspired’ the attack from Islamic State, which then hailed him as a ‘soldier’.
No wonder that Peter Beaumont agonises over ‘a new kind of terror – one we can’t define‘, where the systematic recruitment, training and organisation of other terrorist attacks bleeds into the savage violence of the ‘lone wolf’ prowling undetected in the darkness. The incorporation and adulation of individuals and small groups with no previous connection to IS or other jihadi groups reverses what he calls the standard ‘polarity of responsibility: encouraging acts of violence that it accepts as bloody tributes thrown at its feet.’
The link with petty crime is not surprising. Scott Atran notes that
Serious jihadi involvement with petty criminal networks began after the September 11 attacks as an unintended consequence of the ability of the United States and allies to cut off the flow of funding to suspect groups, especially through Islamic charities. So al-Qaeda and others began looking for funding and arms in criminal networks instead. And in these networks there were large numbers of marginalized immigrant youth, especially in France.
Indeed, Joseph Micallef makes a plausible case for IS expanding its involvement in criminality as its territorial hold on Iraq and Syria comes under intensifying assault: ‘The smuggling networks that are used to bring in armaments and militants can be just as easily be used to traffic in drugs and illegal immigrants.’ His inclusion of ‘illegal immigrants’ should give us pause for thought; I have no idea if he intends this to include refugees from the turmoil in Iraq, Syria and Libya (it shouldn’t). But to the extent that IS is involved in human trafficking then this is a double victimisation of its prey.
All of this may be granted; but a causal link between Lahouaiej-Bouhlel’s murderous drive through crowds of innocent people and the designs of IS or any other radical version of political Islam is proving remarkably elusive. There is a wider debate in France about whether the terrorism serially inflicted upon its people is at root about ‘the radicalization of Islam’ (Gilles Kepel – below left) or the ‘Islamicization of radicalism’ (Olivier Roy – below right) – there is a good summary here – but in this instance it is far from clear that either of them is relevant.

Indeed, Farhad Khorokhavar, a sociologist at the École des Hautes Etudes en Sciences Sociales, doubts that ‘radicalisation’ is the appropriate term at all:
“I don’t think he was radicalised at all… It’s a case of raw violence. He took a decision to kill in a moment of despair. My guess is that it’s much more like a mass shooting in the US than [Islamist] radicalisation.”
He speaks instead of ‘mimetic violence’, where previous attacks have furnished ‘a model that fragile people can imitate.’
So I don’t know whether the atrocity in Nice can be attributed to IS or not – but I have no doubt that the precipitate rush to do so has substantive consequences.
One place to start thinking critically about them is this photograph of a woman consumed by grief as she searches for her son after the attack:

The image serves to remind us that – if, to repeat, this does prove to be an attack whose trail can be traced back, however indirectly, to the dismal doors of Islamic State – the victims of such atrocities include people of many cultures and faiths. Theirs is not a ‘war’ against a single, monolithic enemy; Nice is far from being a homogeneous city – like France, like the rest of Europe – and Alissa Rubin captures what she calls its ‘many-layered’ geography better than most:
There is the Nice of popular imagination, the old-world resort dotted with palm trees and cafes that look out on the Mediterranean Sea, suffused with an incandescent light prized for centuries by artists.
Then there is the other Nice, one that begins to show its face a few blocks inland from the seaside Promenade des Anglais, the majestic arc of a boulevard where 84 people were killed by a 31-year-old Tunisian immigrant at the wheel of a 19-ton truck. This Nice is home to many Muslim immigrants from North Africa, including a secular middle-class that has lived alongside non-Muslim French, and is also a place that local officials estimate has sent as many as 100 young people to fight in Syria with extremists.
“It is rare that these two worlds mix with each other except at the moment of festivities or of agreement, like the gatherings on Saturday,” said Feiza Ben Mohamed of the Muslims of the South, an organization that fights radicalization, referring to the public mourning for those killed in the truck attack.
“Yet the first victim was Muslim, and a good number of the victims were Muslims,” Ms. Mohamed added. “Just yesterday I was on the promenade reflecting on what had happened, and a journalist asked me if I was there to apologize in the name of Muslims. I said to him, ‘No, I came to weep for the dead like everyone else.’”
You can read another (short) essay by Farhad Khorokhavar on these divisions in France, ‘Jihad and the French exception’, here. In Nice they have been intensified, not only by recruiters for the butchery in Syria – and there is no doubt of their success in Nice: Alpes-Maritimes was one of the first French départements to implement a counter-radicalisation strategy of sorts – but also by the advance of the far right National Front, and no doubt by memories of France’s colonial adventures in North Africa and the Levant and its deepening military involvement in Syria.
For now, France seems under repeated attack: the Charlie Hebdo murders in Paris in January 2015; the attacks on the Bataclan and other public places in Paris last November; and now the murder of more than 80 people in Nice.

Each of these mass murders is truly, wrenchingly shocking: but those of us who live in Europe or North America cannot afford to allow those shock-waves to be refracted by geography because this would erect the bloody partition that is one of IS’s central objectives. Nihilism meets narcissism.
I made much the same point about Paris and Beirut last year. Now we might twin Nice with Baghdad. Like Nice – like all cities worthy of the name – Baghdad is far from homogeneous, for all the ethno-sectarian ‘cleansing’ that occurred during the US occupation (see my account of ‘The Biopolitics of Baghdad’: DOWNLOADS tab), and those tensions continue to roil. The truck bombing and subsequent fire that killed 300 people in the Karrada district as they broke their Ramadan fast at the end of the day on 3 July may have seemed like the ‘new normal’ to commentators watching the rising tide of violence in post-occupation Iraq; it too was claimed by IS. So too many of us doubtless shrugged our shoulders.
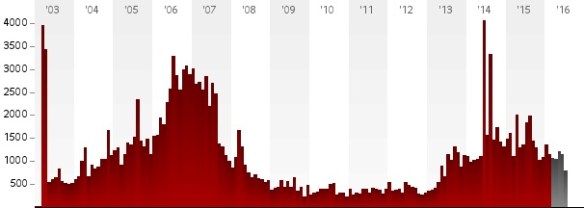
Documented civilian deaths from violence in Iraq 2003-July 2016 (Iraq Body Count)
And yet, as Walaa Chahine so movingly testified after another bombing there on 12 July, ‘We may be used to bombings in Baghdad, but Baghdad isn’t‘:
We are used to it, so we don’t make hashtags, change our profile pictures, or memorize their names. By taking away these rights away from them, and yes, they have become rights, as long as other victims are given them, we are taking away their connection to us as humans. We forget that we would probably never get used to having our hometowns bombed every day, that just like us, they are humans who don’t forget, can’t forget.
No, the eleven people killed today weren’t used to dying. The 292 killed last week were not used to it. Their families will never get used to it. No matter how long you spend in a war area, you never get used to it. Ask a soldier, ask a refugee, ask someone who experiences violence and pain on the daily if they ever truly get used to it. We might be able to tune out their screams, but we weren’t the ones screaming in the first place.

And so, as this contrapuntal geography shows, it bears repeating – until even the tone-deaf Donald Trump gets it – that most of the victims of Islamic State’s terrible violence are other, innocent Muslims. And they live – and die – outside Europe and North America too.