On this terrible morning, with Donald Trump elected as President-designate of the United States, what to say? Wrestling with sleeplessness last night, I started to think about the Statue of Liberty (bear with me). I wrote about its multiple valences more than twenty years ago in Geographical Imaginations:
Frédéric-Auguste Bartholdi‘s original proposal was for a lighthouse in the likeness of a woman to be raised at the Mediterranean entrance to the Suez Canal as a symbol of the nineteenth-century expansion of Europe. Its title, Egypt carrying light to Asia, was intended to assert the historical mission of Europe – with a colonized Egypt acting as its handmaiden – to bring “enlightenment” to the Orient. Bartholdi spent two years making plans and models but in 1869 – the year the Canal opened – the Khedive Ismail withdrew his support and it was not until 1871 that Bartholdi was able to reactivate his scheme.
By then, in the wake of the Pais Commune, the project had been transformed and relocated. One of his patrons, Édouard de Laboulaye, suggested that a monument be raised on the shores of the New World to symbolize Liberty Enlightening the World. The representation of Liberty as a woman derived from classical antiquity, but this ‘whole allegorical apparatus’, as Maurice Agulhon called it, had been codified in France in the late seventeenth century. When the Revolution occurred, Liberty already had an established iconographical status and a decree of 1792 adopted her as the seal of the republic: ‘the image of France in the guise of a woman, dressed in the style of Antiquity, standing upright, her right hand holding a pike surrounded by a Phyrgian cap or cap of liberty.’

By the opening decades of the nineteenth century the use of ‘Marianne’ as a symbol of both Liberty and the Republic had become a commonplace. This was true in the most literal of senses. “Where was this woman to be seen?” ask Agulhon. The answer: “all over the place”. Paris had two statues of her, in the Place de la Concorde and the Place Vendôme, and many other towns had their own effigies. In 1848 she appeared on the second seal of the Republic, wearing a diadem of corn with seven rays of the sun encircling her head in a spiked halo.

The resemblance to the head of the American statue is striking, but a sunburst was also the Bartholdi family emblem and, still more significantly, it was intimately associated with the reign of Louis XIV, the ‘Sun King’. To adorn Liberty with a sunburst was thus in a sense ‘to “crown” her’, Kaja Silverman argues, ‘and thereby align her with a tradition of stable and conservative government.’
That Liberty should be represented by a woman was clearly not without irony. In practice, Joan Landes remarks,
the assault on paternalism was limited by force … and by the redirection of women’ public and sentimental existence into a new allegory of republican, virtuous family life. Liberty herself is a profoundly ironic symbol, a public representation of a polity that sanctioned a limited domestic role for women … If Liberty represented woman, surely it was as an abstract emblem of male power and authority.
The power of patriarchy was reasserted still more forcibly after the fall of the Commune with the triumph of the bourgeois republic and its cult of respectability. As Roger Magraw observed, ‘the official Mariannes who adorned town halls by the 1880s wore a halo of flowers and the motto Concorde, moving towards that anodyne statue which France sent to her fellow capitalist republic as the State of Liberty.’ Anodyne indeed: Silverman argues that Bartholdi virtually erased the corporeality of the body. Thus he ‘completely buries the female form beneath hear classic drapery’ and ‘any thought that a body might nevertheless lurk beneath those folds is abruptly put to flight by the possibility of entering the statue and climbing up inside it.’ She is well aware of the sexual connotations of such a reading, of course, and moves quickly to foreclose them. ‘Liberty is precisely an extension of the desire to “return” to the inside of the fantastic mother’s body,’ she proposes, ‘without having to confront her sexuality in any way.’ Viewed in this light, therefore, Liberty is rendered non-threatening and even ‘safe’.
It was thus from within a many-layered iconographical tradition that Laboulaye’s proposal was made. He was Professor of Comparative Law at the Collège de France and although he never crossed the Atlantic he was regarded as France’s greatest expert on the United States. Like many other republicans at the time, he regarded the United States as a model of the ideal society and he and his companions were convinced that a Statue of Liberty, given by France to America, would symbolize their most cherished principles. For this reason Bartholdi was urged to ensure that the statue should ‘not be liberty in a red cap, striding across corpses with her pike at the port’ – a reference to Delacroix’s famous Liberty guiding the people to the barricades (below) – but ‘the American liberty whose torch is held high not to inflame but to enlighten.’ Bartholdi agreed. ‘Revolutionary Liberty cannot evoke American Liberty,’ he declared, ‘which after a hundred years of uninterrupted existence, should not appear as an intrepid young girl but as a woman of mature years, calm, advancing with the light but sure step of progress.’

For all there enthusiasm of the projects initiators, however, public subscriptions were slow – even Gounod conducting La liberté éclairant le monde at the Paris Opéra brought in a mere 8,000 francs – and in American they were slower still. Bartholdi made a show of offering the statue to Philadelphia and Boston; other American cities submitted bids until at last prominent subscribers in New York were goaded into action.
In 1875 Bartholdi started work in his Paris atelier:
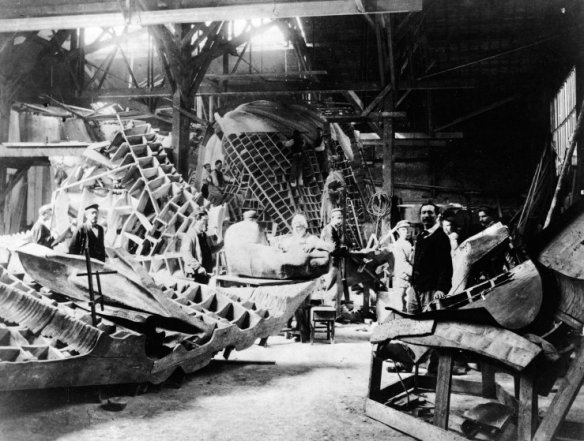
He soon realized the magnitude of the task and invited Gustave Eiffel to design the wrought-iron bracing needed to support the copper sheets that would form the outer skin of the sculpture. It took several years to complete the disembodied sections of the statue, but by the spring of 1883 Bartholdi was at last ready to assemble them. By the end of the year, as Victor Dargaud‘s canvas shows, the statue still surrounded by its scaffolding was looming about the rue de Chazelles.

That same year Emma Lazarus published ‘The New Colossus’ to raise money for the statue’s plinth; its famous lines were eventually mounted inside the lower level:

The government of France presented the Statue of Liberty to the United States on the Fourth of July 1884, and five months later it was dismantled, shipped across the Atlantic and reassembled on Bedloe’s Island in New York harbour.

Astonishingly when the inauguration ceremony was held in October 1886, all women were barred except for the wives of the French delegation (led by Bartholdi). American suffragists held their own simultaneous ceremony, and issued this pointed declaration: ‘In erecting a Statue of Liberty embodied as a woman in a land where no woman has political liberty, men have shown a delightful inconsistency which excites the wonder and admiration of the opposite sex.’
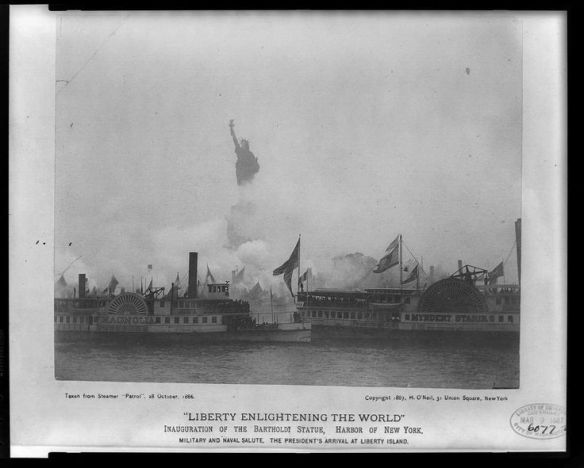

This is only a partial narrative but its echoes this morning are only too sonorous – not least the casual Orientalism, the overpowering whiteness, the complicated sexism and (in blessed counterpoint) Lazarus’s defiant acceptance of the exile and the refugee.
And so, for all the baggage carried by Liberty, if I could draw her now I would show an endless line of refugees; at the very back, a woman in a long flowing dress, her crown askew, using her battered torch as a crutch as she limps along in the dust, hoping against hope to be allowed to cross the border; and on an island in New York Harbor a new, glittering faux-gold statue of a man raising his searchlight in his tiny hands, and on the base Dante‘s immortal instruction: ‘Abandon hope, all ye who enter here….’
Yet today of all days we surely cannot afford to abandon hope. Never has it been more urgent for scholars to reach out far beyond the academy, to create and engage new publics, and to help revitalize a critical and participatory political and intellectual culture – one in which knowledge trumps ignorance, compassion hostility and solidarity selfishness.