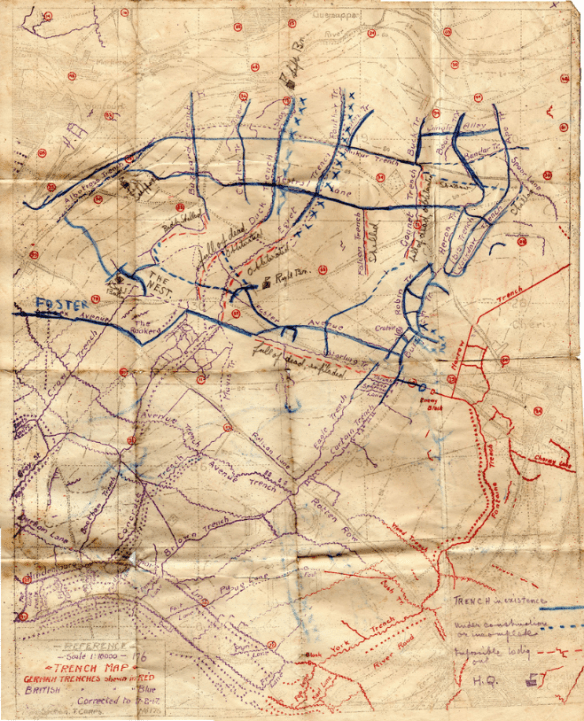
Noam Leshem and Alasdair Pinkerton have embarked on a fascinating new project, Re-inhabiting No Man’s Land: from dead zones to living spaces here:
Nearing the centenary of the First World War, this project explores the ongoing relevance of no-man’s lands in the 21st century. Rather than merely empty, divisive spaces, the project considers the material substance of no-man’s lands, their changing social-cultural meaning and their relevance as productive political and geopolitical spaces.
As a figure of speech, No-Man’s Land is applied to anywhere from derelict inner-city districts and buffer-zones to ‘ungovernable’ regions and tax havens. But what is no-man’s land? What are the conditions that produce it? How is it administered? What sort of human activities do no-man’s lands harbour? These are the questions that prompt us to think about the no-man’s lands not as dead zones, but as living spaces.
News of this arrived from Noam just as I finished the long-form version of Gabriel’s Map: cartography and corpography in modern war, which you can now find under the DOWNLOADS tab (scroll down). Most of the essay is about the First World War on the Western Front (I explain the title at the start of the essay; it comes from William Boyd‘s Ice-Cream War and, in particular, the First World War in East Africa, and the title of this post comes from Edward Lynch‘s Somme Mud: the experiences of an infantryman in France, 1916-1919), but I also end with these reflections on the 21st century:
In this essay I have been concerned with the First World War but, as we approach its centenary, it is worth reflecting on the ways in which modern warfare has changed – and those in which it has not. Through the constant circulation of military imagery and its ghosting in video games, many of us have come to think of contemporary warfare as optical war hypostatised: a war fought on screens and through digital images, in which full motion video feeds from Predators and Reapers allow for an unprecedented degree of remoteness from the killing fields. In consequence, perhaps, many of us are tempted to think of the wars waged by advanced militaries, in contrast to the First World War, as ‘surgical’, even body-less. These are wars without fronts, whose complex geometries have required new investments in cartography and satellite imagery, and there have been major advances in political technologies of vision and in the development of a host of other sensors that have dramatically increased the volume of geo-spatial intelligence on which the administration of later modern military violence relies. All of this has transformed but not replaced the cartographic imaginary.
And yet, for all of their liquid violence, these wars are still shaped and even confounded by the multiple, acutely material environments through which they are fought. In Sebastian Junger’s remarkable despatch from Afghanistan, he notes that for the United States and its allies ‘the war diverged from the textbooks because it was fought in such axle-breaking, helicopter-crashing, spirit-killing, mind-bending terrain that few military plans survive intact for even an hour.’ If that sounds familiar, then so too will Kenneth MacLeish’s cautionary observations about soldiers as both vectors and victims of military violence:
‘The body’s unruly matter is war’s most necessary and most necessarily expendable raw material. While many analyses of US war violence have emphasized the technologically facilitated withdrawal of American bodies from combat zones in favour of air strikes, smart bombs, remotely piloted drones, and privately contracted fighting forces, the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan could not carry on without the physical presence of tens of thousands of such bodies…
In consequence, the troops have had to cultivate an intrinsically practical knowledge that, while its operating environment and technical armature are obviously different, still owes much to the tacit bodily awareness of the Tommy or the Poilu:
‘In the combat zone there is a balance to be struck, a cultivated operational knowledge, that comes in large part from first-hand experience about what can hurt you and what can’t… So you need not only knowledge of what the weapons and armor can do for you and to you but a kind of bodily habitus as well – an ability to take in the sensory indications of danger and act on them without having to think too hard about it first. When you hear a shot, is it passing close by? Is it accurate or random? Is it of sufficient caliber to penetrate your vest, the window of your Humvee or the side of your tank?’
In the intricate nexus formed by knowledge, space and military power, later modern war still relies on cartographic vision – and its agents still produce their own corpographies.
The notes contain various references to No Man’s Land in the First World War, though I’m increasingly interested in what lies on either side. One of the reasons so many commentators seem to think that ‘war among the people’ is a recent development is that the imagery of the Western Front draws the eye again and again to No Man’s Land, but behind the front lines on either side were farms, fields, villages and small towns where people continued to live and work amongst the shelling, the gas attacks, and the billeted troops.
As usual, I’d welcome any comments/criticisms/suggestions on the (I hope near final) draft of the essay: an extended version will appear in War material.