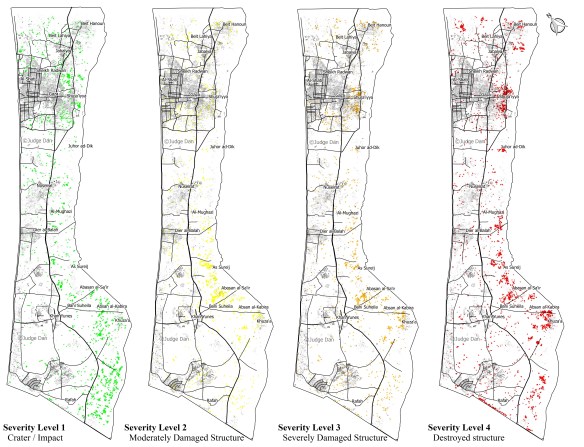
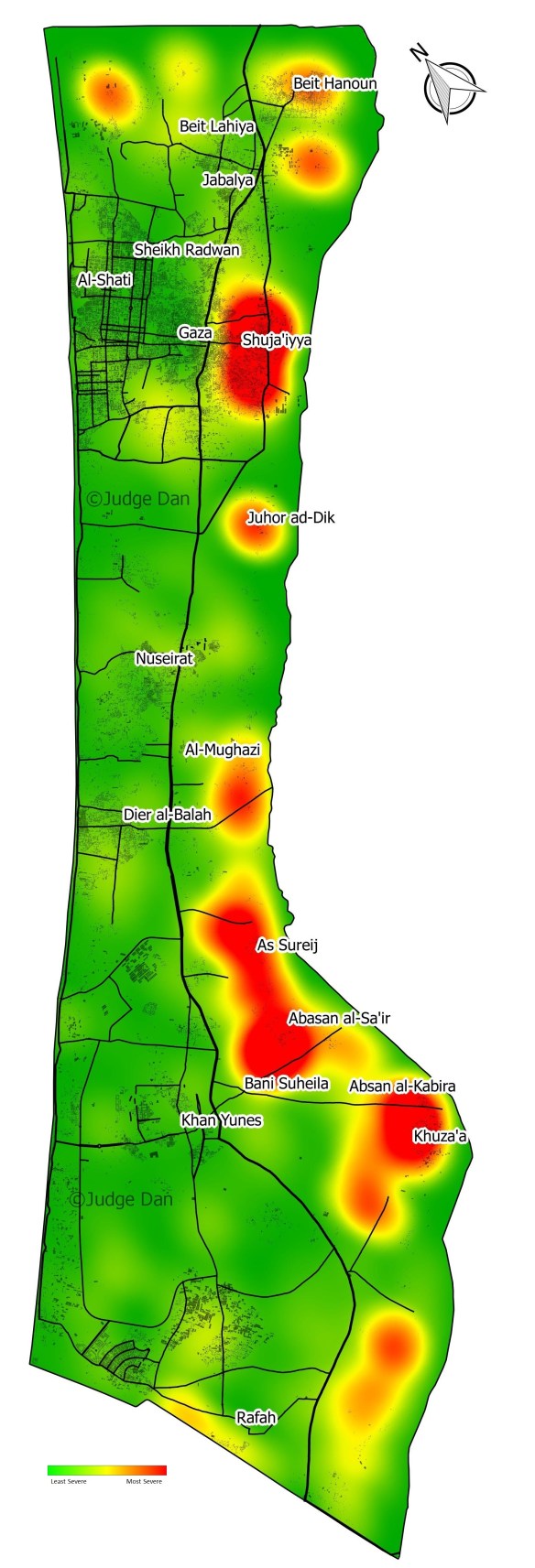
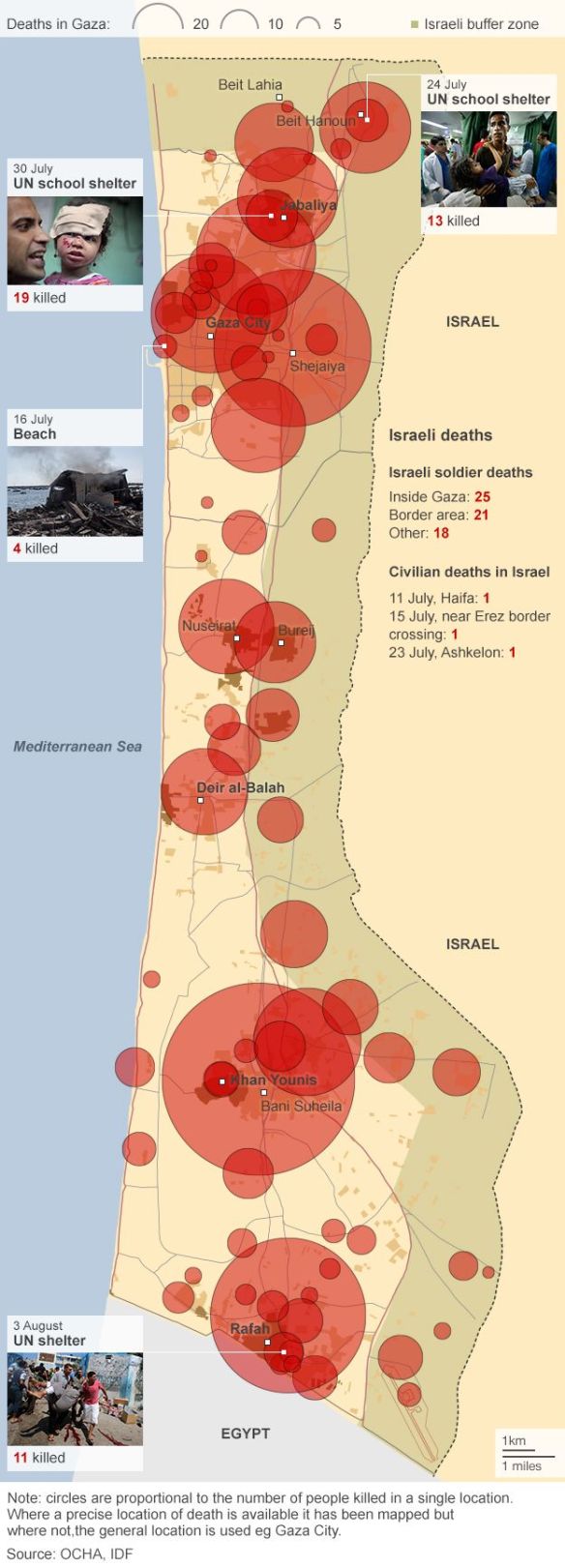
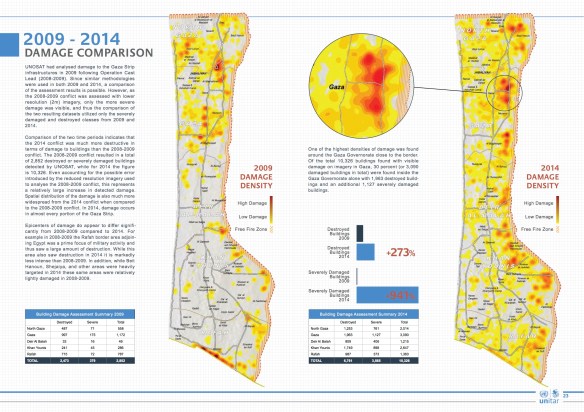
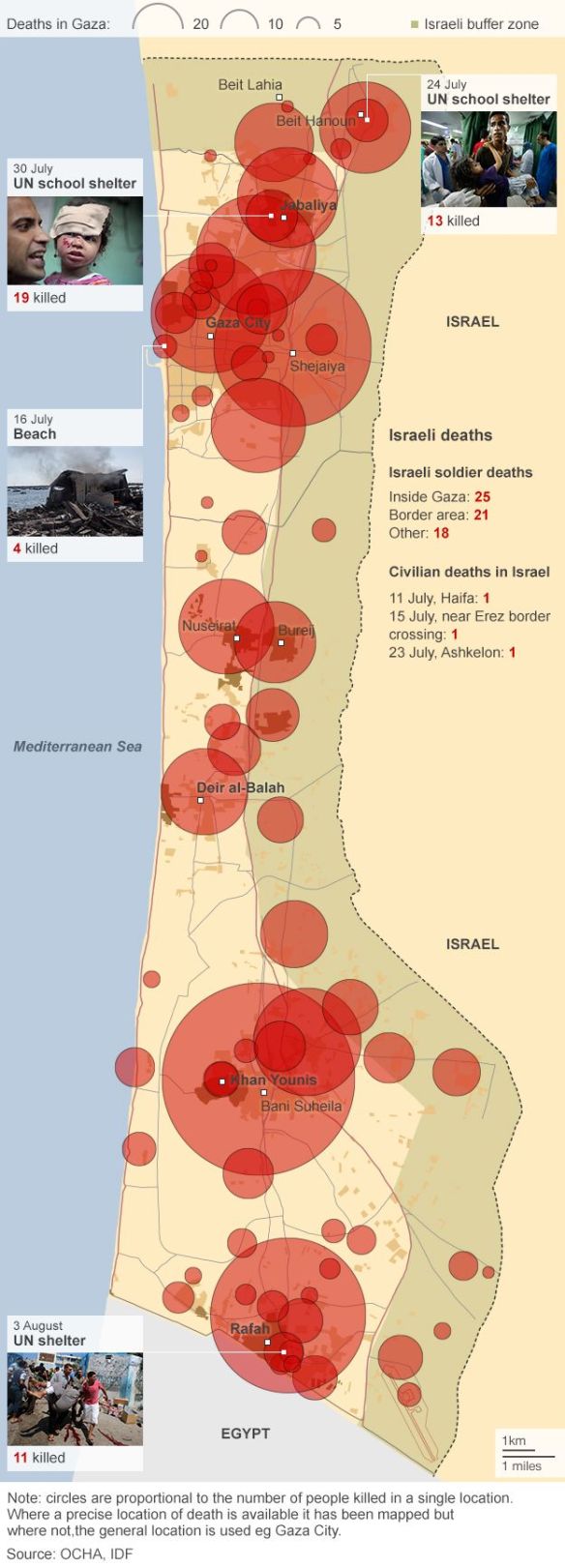
Several recent contributions on military drones – what Forensic Architecture calls Unmanned Aerial Violence – you might be interested in.
First, Steve Coll has a long essay in the latest New Yorker on ‘The Unblinking Stare‘ (and, yes, I do know that those watching the screens blink. Duh) about the drone war in Pakistan. Many readers will remember that it was the New Yorker that published Jane Mayer‘s classic essay on ‘The Predator War‘ (26 October 2009), so it’s high time for an up-date since so much has happened since then. It’s a very helpful survey. Much of it will not be news, but Steve does provide some interesting background to the deadly gavotte between the US and Pakistan (what I’ve called ‘dirty dancing‘; see also here):
Pakistan’s generals and politicians, who come mainly from the country’s dominant, more developed province of Punjab, treated Waziristan’s residents “as if they were tribes that were living in the Amazon,” the journalist Abubakar Siddique, who grew up in the region and is the author of “The Pashtun Question,” told me.
In 2002, Musharraf sent Pakistan’s Army into South Waziristan to quell Al Qaeda and local sympathizers. In 2004, the Army intensified its operations, and, as violence spread, Musharraf allowed the C.I.A. to fly drones to support Pakistani military action. In exchange, Musharraf told me, the Bush Administration “supplied us helicopters with precision weapons and night-operating capability.” He added, “The problem was intelligence collection and targeting. . . . The Americans brought the drones to bear.”
Musharraf allowed the C.I.A. to operate drones out of a Pakistani base in Baluchistan. He told me that he often urged Bush Administration officials, “Give the drones to Pakistan.” That was not possible, he was told, “because of high-technology transfer restrictions.”
We know that close co-operation and even co-ordination between Washington and Islamabad was still the order of the day until at least 2011. We know, too, that local people live under a double threat, and the essay reports on a group interview in Islamabad with half a dozen young men, mainly university students, from Waziristan. On one side, recalling the Stanford/NYU ‘Living under drones‘ report:
Being attacked by a drone is not the same as being bombed by a jet. With drones, there is typically a much longer prelude to violence. Above North Waziristan, drones circled for hours, or even days, before striking. People below looked up to watch the machines, hovering at about twenty thousand feet, capable of unleashing fire at any moment, like dragon’s breath. “Drones may kill relatively few, but they terrify many more,” Malik Jalal, a tribal leader in North Waziristan, told me. “They turned the people into psychiatric patients. The F-16s [of the Pakistan Air Force] might be less accurate, but they come and go.”
On the other side:
Families in North Waziristan typically live within large walled compounds. Several brothers, their parents, and their extended families might share a single complex. Each compound may contain a hujra, or guesthouse, which usually stands just outside the main wall. In the evening, men gather there to eat dinner and talk war and politics. A rich man signals his status by building a large hujra with comfortable guest rooms for overnight visitors. The less well-heeled might have a hujra with just two rooms, carpets, rope cots, and cushions.
Taliban and Al Qaeda commanders moved from hujra to hujra to avoid detection. The available records of drone strikes make clear that the operators would regularly pick up commanders’ movements, follow them to a hujra attached to a private home, watch for hours—or days—and then fire. Many documented strikes took place after midnight, when the target was presumably not moving, children were asleep, and visitors would have returned home.
North Waziristan residents and other Pakistanis I spoke with emphasized how difficult it would be for a drone operator to distinguish between circumstances where a Taliban or Al Qaeda commander had been welcomed into a hujra and where the commander had bullied or forced his way in. If the Taliban “comes to my hujra and asks for shelter, you have no choice,” Saleem Safi, a journalist who has travelled extensively in Waziristan, told me. “Now a potential drone target is living in a guest room or a guesthouse on your compound, one wall away from your own house and family.”
“You can’t protect your family from a strike on a hujra,” another resident of North Waziristan said. “Your children will play nearby. They will even go inside to play.” The researcher in Islamabad said, “There is always peer pressure, tribal pressure, to be hospitable.” He went on, “If you say no, you look like a coward and you lose face. Anyway, you can’t say no to them. If a drone strike does take place, you are a criminal in the courts of the Taliban,” because you are suspected of espionage and betrayal. “You are also a criminal to the government, because you let the commander sleep in your hujra.” In such a landscape, the binary categories recognized by international law—combatant or noncombatant—can seem inadequate to describe the culpability of those who died. Women, children, and the elderly feel pressure from all sides. A young man of military age holding a gun outside a hujra might be a motivated Taliban volunteer, a reluctant conscript, or a victim of violent coercion.
This speaks directly to a general point made by Christiane Wilke: in today’s wars the requirement that combatants identify themselves as combatants (a standard obligation of international humanitarian law) has effectively been transferred to civilians, so that it becomes their responsibility to make themselves known as non-combatants. Even to an unblinking eye at 20,000 feet.

Second, this week the Telegraph carried a video and an interview with ‘Major Yair’, the pseudonym for the pilot of a Israeli Heron TP drone based near Tel Aviv. He reports that roughly 65 per cent of Israeli air operations are conducted by drones. ‘Yair’ served in all three Israeli assaults on Gaza and he says nothing about Israel’s targeted killing – the focus is on the provision of Close Air Support. But the claims he makes will be all too familiar to those familiar with USAF air strikes in Afghanistan:
As Israeli ground units pressed into Gaza, they would call Major Yair for close air support. “They’d be saying ‘we keep getting fire from within those buildings’ and I’m sitting at a distance – on a neat floorspace with screens and air conditioning systems – but you’re sweating and it’s ‘what do I do, what do I do’? How do I not cause more damage than help?”
I’ve repeatedly noted the affinity – even proximity – USAF crews working out of Creech Air Force Base in Nevada feel with troops on the ground in Afghanistan. But ‘Yair’ doesn’t elaborate on the Israeli ground assault. Instead, remarkably, persistently – unblinkingly, you might say – he circles around his own last sentence:
Major Yair stressed how he was constrained by rules of engagement designed to avoid innocent deaths. Hamas operatives, he added, routinely exploited this restraint by hiding behind civilians. One sequence shot by a Heron showed four men preparing to launch a salvo of rockets under a screen of trees. Seconds later, the men were shown running to a nearby street filled with children.
“They’re untouchable now,” said Major Yair, pointing at the screen. “I know that no mission commander, under current directions given by the chief of staff, will engage in this situation. No way.”
He added: “It is sometimes frustrating because you feel that you’re fighting with your hands tied. There are a lot of situations where you see your targets, but you will not engage because they’re next to kindergartens, because they’re driving with their wives and their kids.”

David Blair presses him on the large number of Palestinian civilians killed in Gaza, including children, only to be told:
“We do make mistakes… but it’s nature. People make mistakes. We learn from those mistakes. You’ll see no smiling face after an incident where kids were killed. None of us wants to be in a position where he does these mistakes. We learn and try to avoid this as much as we can.”…
“You learn to live with it,” he said. “It’s not easy. I’ve made mistakes that, for many years, will come back at me. But it’s something that people have to do. It’s not easy. We do not shove it back somewhere in our minds and try to avoid talking about it. We talk about it, we support each other.”
And so, as so often happens in the United States (and elsewhere) too, our gaze is directed away from the victims and towards the torment suffered by those who inflict military violence from the air.
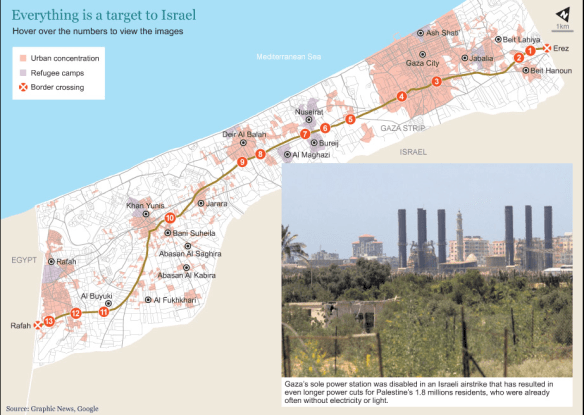
But, third, Corporate Watch has just published the fifth in its series of reports on living under drones in Gaza. These eyewitness reports are indispensable because there are serious problems in using satellite imagery to reconstruct drone strikes. Nobody is better at doing so than Forensic Architecture, but as they note, there is a threshold of detectability:
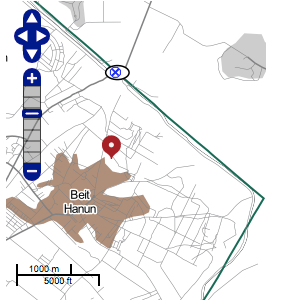
 Some drone-fired missiles can drill a hole through the roof before burrowing their way deep into buildings, where their warheads explode. The size of the hole the missile leaves is smaller than the size of a single pixel in the highest resolution to which publicly-available satellite images are degraded [a square that translate sin to 50 cm by 50 cm of terrain]. The hole is thus at the “threshold of visibility” and might appear as nothing more than a slight color variation, a single darker pixel perhaps. This has direct implications for the documentation of drone strikes in satellite imagery, which is often as close to the scene as most investigators can get. When the figure dissolves into the ground of the image, it is the conditions—legal, political, technical—that degrade the image, or that keep it at a lower resolution that become the relevant material for forensic investigations.
Some drone-fired missiles can drill a hole through the roof before burrowing their way deep into buildings, where their warheads explode. The size of the hole the missile leaves is smaller than the size of a single pixel in the highest resolution to which publicly-available satellite images are degraded [a square that translate sin to 50 cm by 50 cm of terrain]. The hole is thus at the “threshold of visibility” and might appear as nothing more than a slight color variation, a single darker pixel perhaps. This has direct implications for the documentation of drone strikes in satellite imagery, which is often as close to the scene as most investigators can get. When the figure dissolves into the ground of the image, it is the conditions—legal, political, technical—that degrade the image, or that keep it at a lower resolution that become the relevant material for forensic investigations.
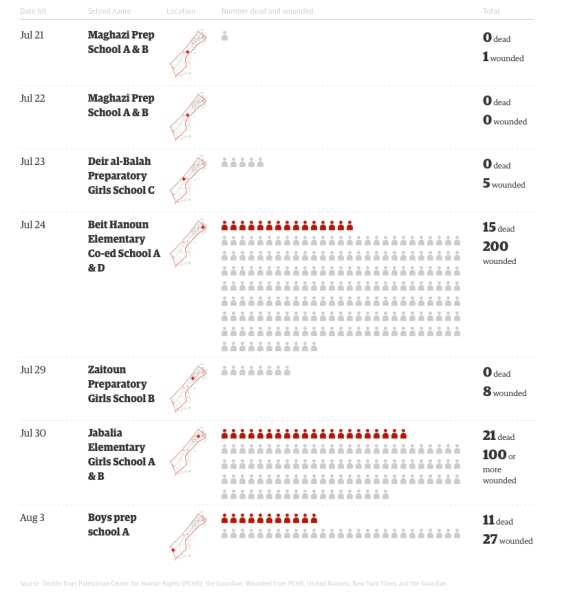
The Corporate Watch report also includes a remarkable tabulation from the Al Mezan Centre for Human Rights in Gaza, showing the numbers of people killed by the Israeli military in Gaza (col. 2) and the proportion killed by drone strikes (col. 3):
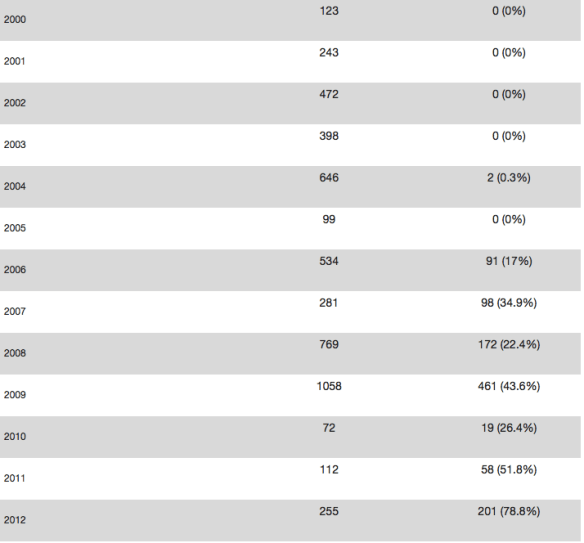
I’m not sure what the sources for these tabulations might be: as Craig Jones has emphasised in a vitally important post, it’s exceptionally difficult to parse Israel’s targeted killings in occupied Palestine, and while these tabulations clearly include many other situations I have no idea how you begin to separate different killing machines in what is, after all, a networked mode of military violence in which drones are likely to perform vital surveillance operations for strikes carried out from other platforms. But the increased reliance on drones chimes with the report from David Blair.
 News from the ever enterprising OR Books of Norman Finkelstein‘s new and superbly titled book, Method and Madness: the hidden story of Israel’s assaults on Gaza. (There’s a delay in ordering this via Amazon or even the Book Depository, so if you want it before next spring you’ll need to get it directly from OR).
News from the ever enterprising OR Books of Norman Finkelstein‘s new and superbly titled book, Method and Madness: the hidden story of Israel’s assaults on Gaza. (There’s a delay in ordering this via Amazon or even the Book Depository, so if you want it before next spring you’ll need to get it directly from OR).