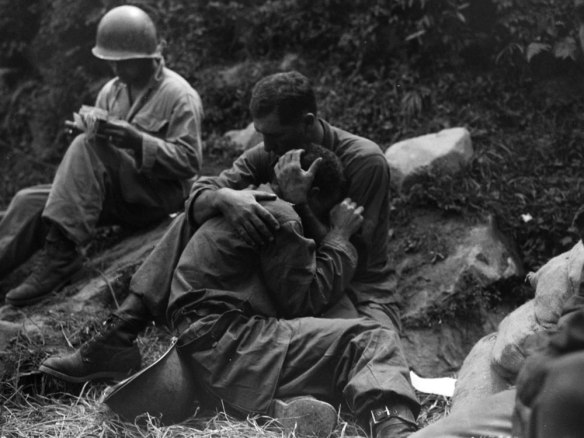
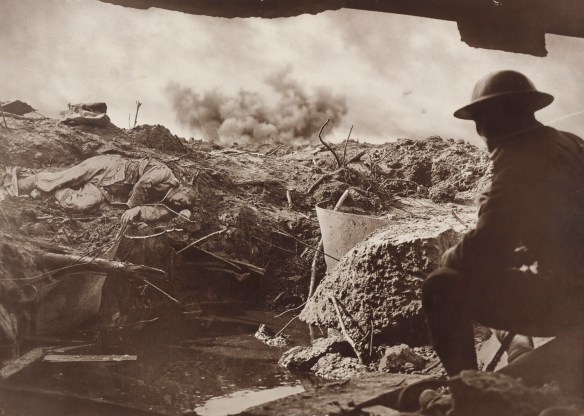
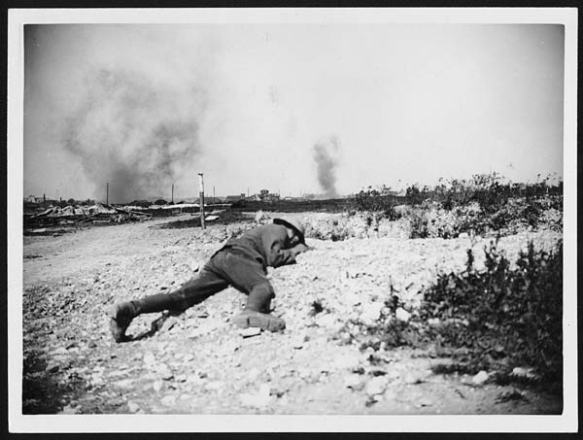
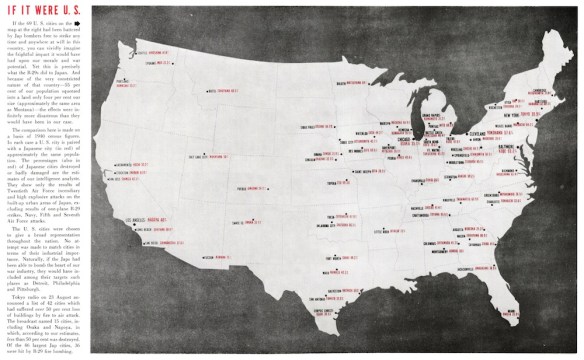
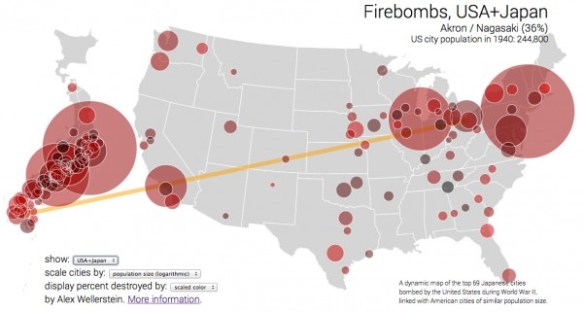
It’s the bleakest of anniversaries – the bombing of Hiroshima 70 years ago today – and there is no shortage of commentary (see, for example, here and here). John Hersey‘s book-length essay on Hiroshima, which filled most of the 31 August 1946 issue of the New Yorker and has been republished online here.
At exactly fifteen minutes past eight in the morning, on August 6, 1945, Japanese time, at the moment when the atomic bomb flashed above Hiroshima, Miss Toshiko Sasaki, a clerk in the personnel department of the East Asia Tin Works, had just sat down at her place in the plant office and was turning her head to speak to the girl at the next desk. At that same moment, Dr. Masakazu Fujii was settling down cross-legged to read the Osaka Asahi on the porch of his private hospital, overhanging one of the seven deltaic rivers which divide Hiroshima; Mrs. Hatsuyo Nakamura, a tailor’s widow, stood by the window of her kitchen, watching a neighbor tearing down his house because it lay in the path of an air-raid-defense fire lane; Father Wilhelm Kleinsorge, a German priest of the Society of Jesus, reclined in his underwear on a cot on the top floor of his order’s three-story mission house, reading a Jesuit magazine, Stimmen der Zeit; Dr. Terufumi Sasaki, a young member of the surgical staff of the city’s large, modern Red Cross Hospital, walked along one of the hospital corridors with a blood specimen for a Wassermann test in his hand; and the Reverend Mr. Kiyoshi Tanimoto, pastor of the Hiroshima Methodist Church, paused at the door of a rich man’s house in Koi, the city’s western suburb, and prepared to unload a handcart full of things he had evacuated from town in fear of the massive B-29 raid which everyone expected Hiroshima to suffer. A hundred thousand people were killed by the atomic bomb, and these six were among the survivors. They still wonder why they lived when so many others died. Each of them counts many small items of chance or volition—a step taken in time, a decision to go indoors, catching one streetcar instead of the next—that spared him. And now each knows that in the act of survival he lived a dozen lives and saw more death than he ever thought he would see. At the time, none of them knew anything.
It’s worth comparing this with the opening scene of Kamila Shamsie‘s brilliant novel Burnt Shadows which imagines the second atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki three days later. Given the map I reproduce below, it’s also worth reading her short essay on the effect of using Google Earth to ‘map’ the bombing here; and since Nagasaki too often disappears from critical view, try Susan Southard‘s recently published Nagasaki: life after nuclear war (Viking/Penguin, 2015) – you can read a long extract here and here.
For a brave attempt to bring the the two bombings into the same narrative frame, see Paul Ham‘s Hiroshima Nagasaki (2012/2014): there’s a helpful review essay by H. Bruce Franklin here, and The Atlantic has just published an extract, ‘The bureaucrats who singled out Hiroshima for destruction’ here.
Joyce C. Stearns, a scientist representing the Air Force, named the four shortlisted targets in order of preference: Kyoto, Hiroshima, Yokohama, and Kokura. They were all “large urban areas of more than three miles in diameter;” “capable of being effectively damaged by the blast;” and “likely to be unattacked by next August.”… Tokyo had been struck from the list because it was already “rubble,” the minutes noted…
Captain William “Deak” Parsons, associate director of Los Alamos’s Ordnance Division, gave another reason to drop the bomb on a city center: “The human and material destruction would be obvious.” An intact urban area would show off the bomb to great effect. Whether the bomb hit soldiers, ordnance, and munitions factories, while desirable from a publicity point of view, was incidental to this line of thinking—and did not influence the final decision.
(You’ll have to read the extract to see why Kyoto was eventually removed from the list).
For subsequent analysis, a good place to start is Alex Wellerstein‘s Restricted Data: the nuclear secrecy blog, which includes a series of excellent posts on sources and visualizations, on the Manhattan Project and what happened at Los Alamos, and most recently an essay which asks ‘Where there alternatives to the atomic bombings?‘ and gives lots of background to those terrible events.
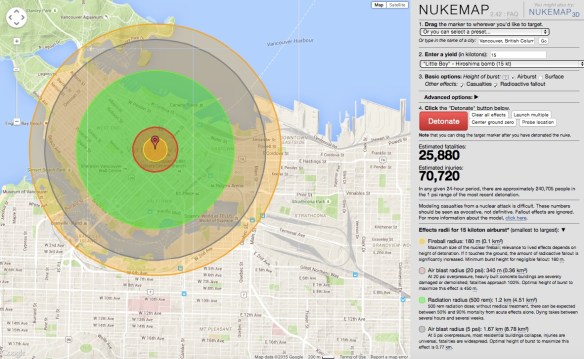
Among Alex’s visualizations is NUKEMAP, which simulates the dropping of ‘Little Boy’ on other towns and cities. Here is downtown Vancouver (for a discussion of airbursts, see Alex’s post here).
Elsewhere, there’s a special issue of Critical Military Studies on the anniversary, and all the articles are open access:
The most modern city in the world: Isamu Noguchi’s cenotaph controversy and Hiroshima’s city of peace: Ran Zwigenberg
Unbearable light/ness of the bombing: normalizing violence and banalizing the horror of the atomic bomb experiences: Yuki Miyamoto
Remembering nukes: collective memories and countering state history: Stefanie Fishel
Contested spaces of ethnicity: zainichi Korean accounts of the atomic bombings: Erik Ropers
Hiroshima and two paradoxes of Japanese nuclear perplexity: Thomas E. Doyle II
Re-imagining Hiroshima in Japan: elin o’Hara slavik
Memory and survival in everyday textures – Ishiuchi Miyako’s Here and Now: Atomic Bomb Artifacts, ひろしま/ Hiroshima 1945/2007: Makeda Best
Nagasaki Re-Imagined: the last shall be first: Kathleen Sullivan
There’s also a special issue of Thesis Eleven, (August 2015: 129 (1)) edited by Brad Evans and Keith Tester in association with the Histories of Violence ‘Disposable Life’ project; articles include:
Susan Neiman, Forgetting Hiroshima, remembering Auschwitz: Tales of two exhibits
Keith Tester, Hiroshima: Remembering and forgetting, everything and nothing
Michael J Shapiro, Hiroshima temporalities
Maja Zehfuss, (Nuclear) war and the memory of Nagasaki: Thinking at the (impossible) limit
Hiro Saito, The A-bomb victims’ plea for cosmopolitan commemoration: Toward reconciliation and world peace
Arne Johan Vetlesen, Post-Hiroshima reflections on extinction
Henry A Giroux, Hiroshima and the responsibility of intellectuals: Crisis, catastrophe, and the neoliberal disimagination machine
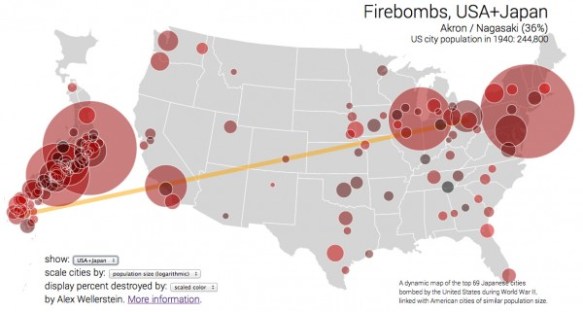
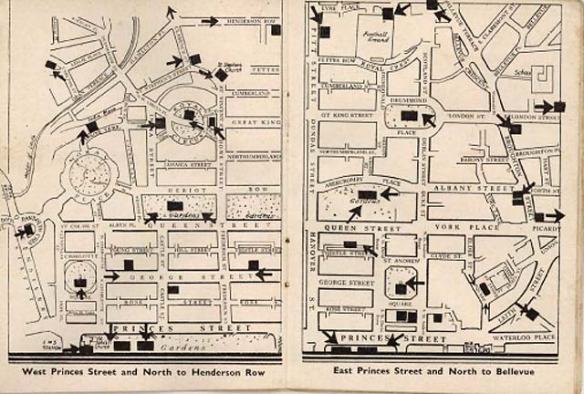
I have just two things to add. The first is to draw attention to the firebombing of Japanese cities that preceded Hiroshima and Nagasaki (Alex compares them in an interesting commentary here and provides a series of compelling comparative interactives here: I’ve pasted an example below, and provided a short commentary here).
In fact, as my quotation from Paul Ham reveals, Hiroshima and Nagasaki were targeted precisely because they had been left alone during the previous attacks and would provide effective laboratories to test the effects of nuclear blasts. On the firebombing campaign, see the painstaking work of Cary Karacas and his colleagues here (my commentaries on the project are here and here; see also their essay on the firebombing of Tokyo and its legacy here); their website includes both a Hiroshima archive and a Nagasaki archive.
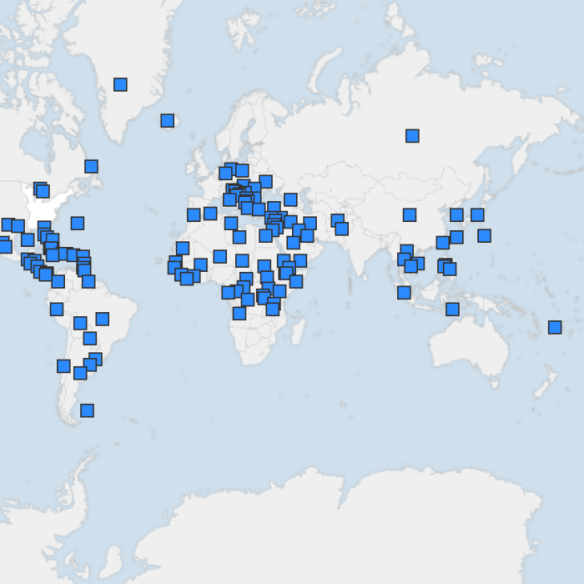
Second, I’ve emphasised the comparative effort to ‘bring the war home’, to imagine the effects of Little Boy and Fat Man on other cities around the world. There are obvious dangers in such an exercise – is our capacity for empathy so limited than we have to rely on a sort of critical narcissism: ‘imagine if it happened to us‘? – but perhaps the most significant objection is that such cartographic conceits can erase not only the bodies incinerated and maimed (through the very abstraction of cartography) but also the racialization of these unmarked bodies. In the characteristically thoughtful introduction to his new book, Tense Future: Modernism, Total War, Encyclopedic Form (2015), Paul K. Saint Amour writes about ‘traumatic earliness’ – about the sense of anticipation, foreboding or bukimi that gripped the people of Hiroshima in the months before their collective deaths: that ‘uneasy combination of continued good fortune [escaping the firebombing] and expectation of catastrophe’. But the ground had already been prepared in the United States, not only scientifically – the endless calculations, calibrations and experiments at Los Alamos – but also culturally.
Michael Sherry‘s The rise of American Air Power: the creation of Armageddon (1987) and Paul Williams‘s Race, ethnicity and nuclear war (2011) are indispensable here – and there’s a sharp, contemporary commentary from Arthur Chu here – but a vivid example is provided by Alex de Seversky‘s Victory through Air Power (1942) and, in particular, its celebration in Walt Disney‘s film version released in 1943. For Disney, there was not only ‘a thrill in the air’ but an exuberant delight at death and destruction on the Japanese ground. You can watch the whole thing below (or on YouTube) but to see what I mean start at 1.07 and watch right through the bombing to the anthropomorphism of the American eagle and the Japanese octopus that follows it. There’s also a short commentary by Henry Giroux here.
Note: My title is taken from this poem by Yukiko Hayashi; if you click on nothing else, please click on this.