News from Lucy Suchman of a special issue of Science, Technology and Human Values [42 (6) (2017)] on Tracking and targeting: sociotechnologies of (in)security, which she’s co-edited with Karolina Follis and Jutta Weber.
Here’s the line-up:
Lucy Suchman, Karolina Follis and Jutta Weber: Tracking and targeting
This introduction to the special issue of the same title sets out the context for a critical examination of contemporary developments in sociotechnical systems deployed in the name of security. Our focus is on technologies of tracking, with their claims to enable the identification of those who comprise legitimate targets for the use of violent force. Taking these claims as deeply problematic, we join a growing body of scholarship on the technopolitical logics that underpin an increasingly violent landscape of institutions, infrastructures, and actions, promising protection to some but arguably contributing to our collective insecurity. We examine the asymmetric distributions of sociotechnologies of (in)security; their deadly and injurious effects; and the legal, ethical, and moral questions that haunt their operations.
Karolina Follis: Visions and transterritory: the borders of Europe
This essay is about the role of visual surveillance technologies in the policing of the external borders of the European Union (EU). Based on an analysis of documents published by EU institutions and independent organizations, I argue that these technological innovations fundamentally alter the nature of national borders. I discuss how new technologies of vision are deployed to transcend the physical limits of territories. In the last twenty years, EU member states and institutions have increasingly relied on various forms of remote tracking, including the use of drones for the purposes of monitoring frontier zones. In combination with other facets of the EU border management regime (such as transnational databases and biometrics), these technologies coalesce into a system of governance that has enabled intervention into neighboring territories and territorial waters of other states to track and target migrants for interception in the “prefrontier.” For jurisdictional reasons, this practice effectively precludes the enforcement of legal human rights obligations, which European states might otherwise have with regard to these persons. This article argues that this technologically mediated expansion of vision has become a key feature of post–cold war governance of borders in Europe. The concept of transterritory is proposed to capture its effects.
Christiane Wilke: Seeing and unmaking civilians in Afghanistan: visual technologies and contested professional visions
While the distinction between civilians and combatants is fundamental to international law, it is contested and complicated in practice. How do North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) officers see civilians in Afghanistan? Focusing on 2009 air strike in Kunduz, this article argues that the professional vision of NATO officers relies not only on recent military technologies that allow for aerial surveillance, thermal imaging, and precise targeting but also on the assumptions, vocabularies, modes of attention, and hierarchies of knowledges that the officers bring to the interpretation of aerial surveillance images. Professional vision is socially situated and frequently contested with communities of practice. In the case of the Kunduz air strike, the aerial vantage point and the military visual technologies cannot fully determine what would be seen. Instead, the officers’ assumptions about Afghanistan, threats, and the gender of the civilian inform the vocabulary they use for coding people and places as civilian or noncivilian. Civilians are not simply “found,” they are produced through specific forms of professional vision.
Jon Lindsay: Target practice: Counterterrorism and the amplification of data friction
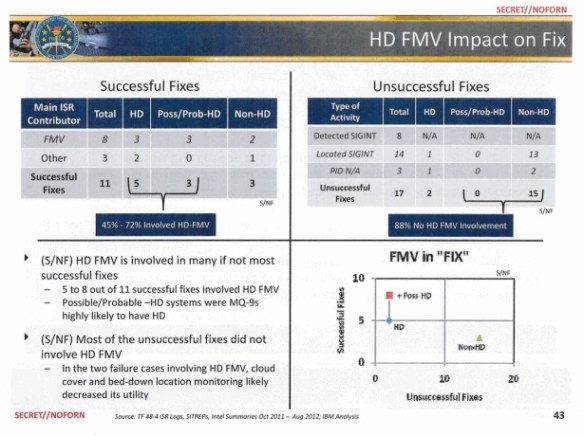
The nineteenth-century strategist Carl von Clausewitz describes “fog” and “friction” as fundamental features of war. Military leverage of sophisticated information technology in the twenty-first century has improved some tactical operations but has not lifted the fog of war, in part, because the means for reducing uncertainty create new forms of it. Drawing on active duty experience with an American special operations task force in Western Iraq from 2007 to 2008, this article traces the targeting processes used to “find, fix, and finish” alleged insurgents. In this case they did not clarify the political reality of Anbar province but rather reinforced a parochial worldview informed by the Naval Special Warfare community. The unit focused on the performance of “direct action” raids during a period in which “indirect action” engagement with the local population was arguably more appropriate for the strategic circumstances. The concept of “data friction”, therefore, can be understood not simply as a form of resistance within a sociotechnical system but also as a form of traction that enables practitioners to construct representations of the world that amplify their own biases.
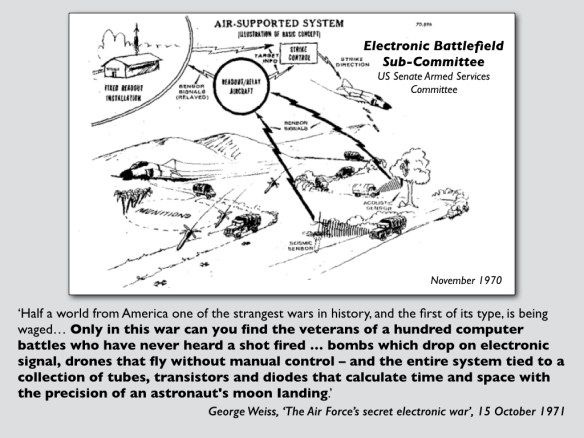
M.C. Elish: Remote split: a history of US drone operations and the distributed labour of war
This article analyzes US drone operations through a historical and ethnographic analysis of the remote split paradigm used by the US Air Force. Remote split refers to the globally distributed command and control of drone operations and entails a network of human operators and analysts in the Middle East, Europe, and Southeast Asia as well as in the continental United States. Though often viewed as a teleological progression of “unmanned” warfare, this paper argues that historically specific technopolitical logics establish the conditions of possibility for the work of war to be divisible into discreet and computationally mediated tasks that are viewed as effective in US military engagements. To do so, the article traces how new forms of authorized evidence and expertise have shaped developments in military operations and command and control priorities from the Cold War and the “electronic battlefield” of Vietnam through the Gulf War and the conflict in the Balkans to contemporary deployments of drone operations. The article concludes by suggesting that it is by paying attention to divisions of labor and human–machine configurations that we can begin to understand the everyday and often invisible structures that sustain perpetual war as a military strategy of the United States.
I’ve discussed Christiane’s excellent article in detail before, but the whole issue repays careful reading.
And if you’re curious about the map that heads this post, it’s based on the National Security Agency’s Strategic Mission List (dated 2007 and published in the New York Times on 2 November 2013), and mapped at Electrospaces: full details here.