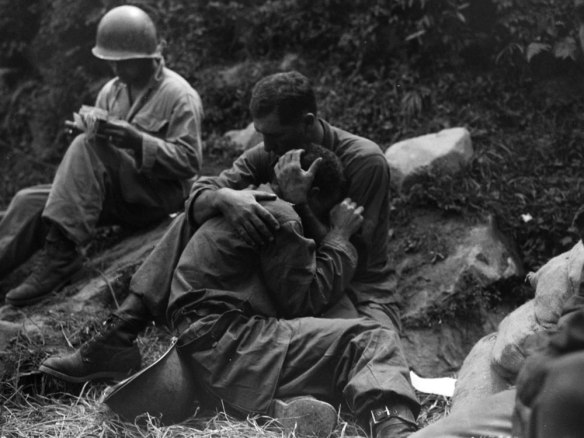
Since I added ‘The Natures of War’ to the DOWNLOADS section several people have asked me about my use of novels, especially in relation to Vietnam, while others have asked me to recommend writings – both novels and memoirs – that treat contemporary conflicts, especially Afghanistan.

The first part is easy. To say things too quickly, I think the usual distinction between ‘fiction’ and ‘non-fiction’ is much more problematic than it seems (don’t we all know this? and in any case where exactly do you place a ‘memoir’ in such a strangely bifurcated landscape?). I also believe that there are some insights – truths, if you prefer – that are best conveyed in ostensibly fictional form. For that reason I suspect it’s significant that it’s my appeal to (for example) Karl Marlantes‘s magnificent Matterhorn in the Vietnam section that seems to trouble some readers much more than my use of poetry in the section on the Western Desert in the Second World War. Yet both emerged through their authors’ reflections on their experiences of modern war in those places. That doesn’t mean that one can ignore literary conventions or linguistic devices – no text is a transparent reflection of the world, after all – but this surely also holds for nominally factual accounts too (and that goes for military blogs, which have created their own conventions). In other ‘fictional’ cases I can think of – like Tom McCarthy‘s C, which I drew upon in ‘Gabriel’s Map’ to characterise the battlefields of the Western Front – the narrative is clearly embedded in intensive and immensely thoughtful research. In fact, I’d push this further: hence my interest in documentary drama as part of – not simply a product of – the research process.
The second question is more difficult, but there are some recent guides which might help. A good place to start is George Packer‘s ‘Home Fires: how soldiers write their wars‘ which appeared in the New Yorker last spring. Packer tries to pin down what is distinctive about writing that seeks to capture the wars fought in the shadows of 9/11:
‘The first wave of literature by American combatants in these long, inconclusive wars has begun to appear—poems, memoirs, short stories, novels. Their concerns are the same as in all war writing: bravery and fear, the thin line between survival and brutality, the maddening unknowability of the enemy, tenderness, brotherhood, alienation from a former self, the ghosts of the past, the misfit of home.
But Iraq was also different from other American wars… Without a draft, without the slightest sacrifice asked of a disengaged public, Iraq put more mental distance between soldiers and civilians than any war of its duration that I can think of. The war in Iraq, like the one in Vietnam, wasn’t popular; but the troops, at least nominally, were—wildly so. (Just watch the crowd at a sports event if someone in uniform is asked to stand and be acknowledged.) Both sides of the relationship, if they were being honest, felt its essential falseness.’
Given this disconnect, he concludes, ‘it’s not surprising that the new war literature is intensely interested in the return home.’ But when it deals with the soldiers’ experience of war, he continues,
‘It deals in particulars, which is where the heightened alertness of combatants has to remain, and it’s more likely to notice things. To most foreign observers, the landscape of Iraq is relentlessly empty and ugly, like a physical extension of the country’s trauma. But in the poetry and the prose of soldiers and marines the desert comes to life with birdsong and other noises, the moonlit sand breeds dreams and hallucinations.’
It’s that struggle to turn the experience of land into its evocation that interests me. But Packer makes surprisingly little of it, and his gaze is focused almost unwaveringly on Iraq rather than Afghanistan (not surprising, given his own war reporting).
Writing in the New York Times, Michiko Kakutani identifies a series of writings on the human costs of what Dexter Filkins called ‘the forever war’:
‘War cracks people’s lives apart, unmasks the most extreme emotions, fuels the deepest existential questions. Even as the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan morph into shapeless struggles with no clear ends in sight, they have given birth to an extraordinary outpouring of writing that tries to make sense of it all: journalism that has unraveled the back story of how and why America went to war, and also a profusion of stories, novels, memoirs and poems that testify to the day-to-day realities and to the wars’ ever-unspooling human costs.
‘All war literature, across the centuries, bears witness to certain eternal truths: the death and chaos encountered, minute by minute; the bonds of love and loyalty among soldiers; the bad dreams and worse anxieties that afflict many of those lucky enough to return home. And today’s emerging literature … both reverberates with those timeless experiences and is imprinted with the particularities of the conflicts in Afghanistan and Iraq: changes in technology, the increased presence of female soldiers and, most importantly, the all-volunteer military, which has opened a chasm between soldiers (“the other 1 percent”) and civilians.’
Here too there is an attempt to see how today’s writing differs from the established canon of war literature. En route, Kakutani makes some good suggestions for reading, but she says very little about the differences – those dense ‘particulars’ again – between Iraq and Afghanistan.

She leaves that to Brian Castner‘s outstanding essay for the LA Review of Books, ‘Afghanistan: a stage without a play.’
Castner did two tours in Iraq, and his own account of that experience (and, just as important, what followed) in The Long Walk is a tour de force in every sense of the phrase. But he is also remarkably perceptive in his readings of Afghanistan (‘the Undescribed War’, he calls it) and – of particular interest to me, given my interest in ‘the natures of war’ or what my good friend Gastón Gordillo would prefer me to call ‘terrain‘ – its land and landscapes. Castner also draws several illuminating comparisons with Vietnam (not least through a double parallel with the US’s ‘Indian Wars’ of the nineteenth century).
Kevin Maurer covered both wars, and always found
“Afghanistan far more riveting than Iraq because it’s a whole different world. Baghdad is a Middle Eastern city, but it is a modern city. In Afghanistan that barely exists. I’ve always been able to turn my brain into Afghanistan mode and out, while Iraq blurs.”
The influence of the terrain, especially its beauty, is clear: while a few descriptions of colorful Iraqi skies creep into the literature, it was mostly an ugly urban war fought along the New York State Thruway, rest stop to rest stop. “Afghanistan always had that Vietnam vibe to it,” Maurer said, “because you can go get lost in Afghanistan, you can be on some hill on some outpost. In Iraq you were never that far out.”

And for that very reason the terrain was always more than beautiful. You can see that in a film like Restrepo – and even more clearly in Koregal (above) – but according to Castner you can also see it in John Renehan’s forthcoming novel, The Valley. And here too Vietnam continues to haunt the imaginative landscape:
 The landscape acts as an omnipresent consciousness, an apparition always in the corner of [Lieutenant] Black’s eye, and Renehan attaches to it layers of reverence and dread and unknowable quasi-mysticism; the valley is capable of anything. This infection spreads slowly for the reader, and Renehan says his writing process followed a similar path. “I more or less thought I was setting out to write a mystery story that happened to be set in a war. But as I started writing it I realized it was growing into something different in my mind, and it changed on paper too.” A detective story becomes a heroin- and concussion-fueled dreamscape that crosses genres. “Going After Cacciato gave me comfort in writing the parts of The Valley that become almost surreal,” Renehan said. “It reassured me that this sort of thing is okay, because it’s a war novel, right?”
The landscape acts as an omnipresent consciousness, an apparition always in the corner of [Lieutenant] Black’s eye, and Renehan attaches to it layers of reverence and dread and unknowable quasi-mysticism; the valley is capable of anything. This infection spreads slowly for the reader, and Renehan says his writing process followed a similar path. “I more or less thought I was setting out to write a mystery story that happened to be set in a war. But as I started writing it I realized it was growing into something different in my mind, and it changed on paper too.” A detective story becomes a heroin- and concussion-fueled dreamscape that crosses genres. “Going After Cacciato gave me comfort in writing the parts of The Valley that become almost surreal,” Renehan said. “It reassured me that this sort of thing is okay, because it’s a war novel, right?”
What I need to think more about – the process I started in ‘Gabriel’s Map’ and continued in ‘The Natures of War’ – is how, despite Castner’s title, the stage is always part of the play. And novels and poems will continue to help me do so.
POSTSCRIPT Just after I finished drafting this post, I stumbled across ‘s Peter Molin‘s excellent blog: Time Now: the Iraq and Afghan wars in art, film and literature which also discusses the three reviews I list here. Peter is a US Army officer who served in Afghanistan in 2008-9, and his posts are rich in ideas, insights and resources: well worth bookmarking.