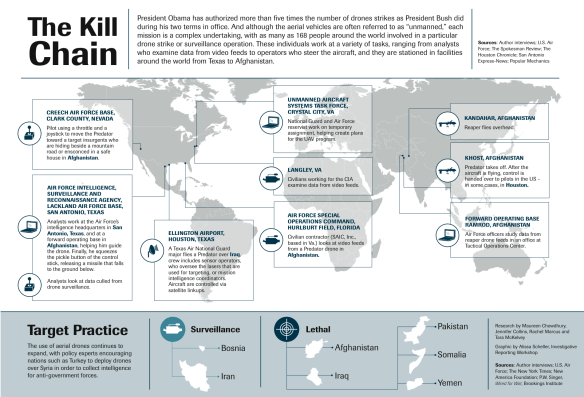
Three contributions to the debates over drones and military violence. First, my friends at the Bard Center for the Study of the Drone have published Dan Gettinger‘s essay on ‘Drone Geography: mapping a system of intelligence‘. It’s a superb sketch of the intelligence network in which the US Air Force’s drones are embedded (you can read my complementary take on ‘Drone geographies’ under the DOWNLOADS tab). Let me add just one map to the illustrations that stud his essay. It’s taken from the Air Force’s RPA Vector report for 2013-28, published last February, and it shows the architecture of remote split operations within and beyond the United States. It’s helpful (I hope) because it shows how the Ground Control Stations in the continental United States feed in to the Distributed Common Ground System that provides image analysis and exploitation (shown in the second map, which appears in a different form in Dan’s essay). I’m having these two maps combined, and I’ll post the result when it’s finished.


Dan is right to emphasise the significance of satellite communications; much of the discussion of later modern war and its derivatives has focused on satellite imagery, and I’ve discussed some of its complications in previous posts, but satellite communications materially shape the geography of remote operations. The Pentagon has become extraordinarily reliant on commercial providers (to such an extent that Obama’s ‘pivot to the Pacific’ may well be affected), and limitations of bandwidth have required full-motion video streams from Predators and Reapers (which are bandwidth hogs) to be compressed and image quality to be degraded. Steve Graham and I are currently working on a joint essay about these issues.
One caveat: this is not the only network in which US remote operations are embedded. In my essay on ‘Dirty Dancing’ (now racing towards the finish line) I argue that the CIA-directed program of targeted killing in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas of Pakistan cannot be severed from the multiple ways in which the FATA have been configured as both borderlands and battlefields and, in particular, from the cascade of military operations that have rendered the FATA as a space of exception (in something both more and less than Agamben’s sense of the term). Here I’ve learned much from an excellent essay by Elizabeth Cullen Dunn and Jason Cons, ‘Aleatory sovereignty and the rule of sensitive spaces’, Antipode 46 (1) (2014) 92-109). They complicate the claim that spaces of exception always derive from a single locus of sovereign power (or ‘the sovereign decision’). Instead, they suggest that borderlands are ‘contested spaces’ where ‘competing’ powers ‘collide’. In the FATA multiple powers have been involved in the administration of military violence, but on occasion – and crucially – they have done so in concert and their watchword has been a qualified and covert collaboration. In particular, the FATA have been marked by a long and chequered gavotte between the militaries and intelligence services of the United States and Pakistan which, since the 1980s, has consistently put at risk the lives of the people of the borderlands. And in my essay on ‘Angry Eyes’ (next on my screen) I argue that the US military’s major use of Predators and Reapers in Afghanistan – orchestrating strikes by conventional aircraft and providing close air support to ‘troops in contact’ – depends on communication networks with ground troops in theatre, and that this dispersed geography of militarised vision introduces major uncertainties into the supposedly ‘precise’ targeting process.
 Second: Elliott Prasse-Freeman has an extended review of the English translation of Grégoire Chamayou‘s Theory of the drone – called ‘Droning On‘ – over at the New Inquiry (you can access my own commentaries on the French edition here: scroll down). His central criticism is this:
Second: Elliott Prasse-Freeman has an extended review of the English translation of Grégoire Chamayou‘s Theory of the drone – called ‘Droning On‘ – over at the New Inquiry (you can access my own commentaries on the French edition here: scroll down). His central criticism is this:
While his title promises theory, we instead are treated to a digression on the military and social ethics of attacks from the air, in which Chamayou asks without irony, “can counterinsurgency rise to the level of an aero-policy without losing its soul?” What offends Chamayou is the “elimination, already rampant but here absolutely radicalized, of any immediate relation of reciprocity” in warfare. This, we are told, is the problem.
Promised a theory of the drone, how do we arrive at a theory of the noble soldier?…
And so, dispatching with the dream of the drone … Chamayou assumes the concerns not of the brutalized but of military leaders and soldiers.
He continues in terms that resonate with my argument in ‘Dirty Dancing’:
By combining knowing (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance), sighting (targeting in movement and in the moment), and eliminating (“putting warheads on foreheads”), the drone constitutes an assemblage of force (as drone-theorist Derek Gregory puts it) that promises a revolution in control and allows the US war apparatus to imagine space and politics in new ways. Because the body of the accused can ostensibly be precisely seen, it can be seen as itself carving out a body-sized exception to state sovereignty over the territory on which that body moves. In this way, eliminating the body does not constitute an assault on the territory of the state, as these bodies are presented as ontologically (and hence quasi-legally) disconnected from that territory. Geographer Stuart Elden in Terror and Territory (2009) points out the significant overlap between who are labeled ‘terrorists’ and movements fighting for their own political spaces – which hence necessarily violate extant states’ ‘territories’ (and hence the entire international order of states): to violate territory is to terrorize. The US is hence remarkably concerned in its arrogation of a position of supra-sovereignty to ensure that it overlaps with ‘classic’ state sovereignty, and by no means violates the norm of territorial integrity (well-defined borders): by harboring or potentially harboring unacceptable transnational desires, the militant uproots himself, and risks being plucked out and vaporized in open space that belongs only to him. The exception to sovereignty provides the drone the opportunity to extend this exception into temporal indefiniteness: wars are not declared, aggressions are not announced—the fleet, fusing police and military functions, merely watches and strikes, constantly pruning the ground of human weeds.
In ‘Dirty Dancing’ I’m trying to prise apart – analytically, at least – the space of exception, conceived as one in which a particular group of people is knowingly and deliberately exposed to death through the political-juridical removal of legal protections and affordances that would otherwise be available to them, and territory conceived (as Stuart suggests) as a political-juridical technology, a series of calculative practices that seeks to calibrate and register a claim over bodies-in-spaces. That’s why Dan Gettinger’s essay is so timely too, and why I’ve been thinking about the FATA as a performance of what Rob Kitchin and Martin Dodge call ‘code/space’, why I’ve been working my way through the files released by Edward Snowden, and why I’ve been thinking so much about Louise Amoore‘s superb critique of The politics of possibility: risk and security beyond probability (2013).

Although Louise doesn’t address drone strikes directly, her arguments are full of vital insights into the networks that are mobilised through them. ‘The sovereign strike is always something more, something in excess of a single flash of decision’, she insists, and when she writes that —
those at risk (which is to say those who are to be put at risk by virtue of their inferred riskiness) are ‘not strictly “included by means of their own exclusion”, as Agamben frames the exception, they are more accurately included by means of a dividuated and mobile drawing of risk fault lines’
 — it’s a very short journey back to Grégoire Chamayou‘s reflections on the strange (in)dividual whose ‘schematic body’ emerges on the targeting screen of the Predator or Reaper. Louise writes of ‘the appearance of an emergent subject’, which is a wonderfully resonant way of capturing the performative practices through which targets are produced: ‘pixelated people’, she calls them, that emerge on screens scanning databanks but which also appear in the crosshairs…
— it’s a very short journey back to Grégoire Chamayou‘s reflections on the strange (in)dividual whose ‘schematic body’ emerges on the targeting screen of the Predator or Reaper. Louise writes of ‘the appearance of an emergent subject’, which is a wonderfully resonant way of capturing the performative practices through which targets are produced: ‘pixelated people’, she calls them, that emerge on screens scanning databanks but which also appear in the crosshairs…
And finally, Corporate Watch has just published a report by Therezia Cooper and Tom Anderson, Gaza: life beneath the drones. This brings together a series of interviews conducted in 2012 – when ‘drones killed more people in Gaza than any other aircraft’ – that were first published in serial form in 2014. The report includes a tabulation of deaths from Israeli military action in Gaza and those killed directly by drones (2000-2014) and a profile of some of the companies involved in Israel’s military-industrial complex.