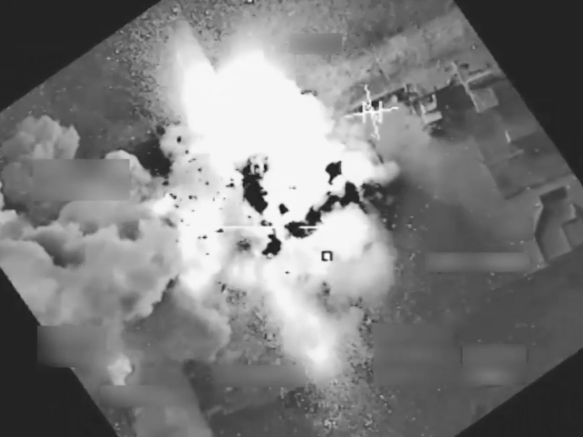
In this second post on Cities under siege I provide a back-story to the re-intensification of military and paramilitary violence against civilians in Syria I described here. But it’s also a back-story to the stunning image above, ‘Deluge’ by Imranovi: people were evacuated to what eventually became nominally ‘de-escalation zones’ from besieged cities like Aleppo, but many more continued to flee Syria altogether – like Imranovi himself (more on Imranovi here and here). It’s worth pausing over his artwork: every time we see video of those perilous boats crammed with desperate refugees we ought to reflect on the oceans of bloody rubble strewn across their land and the millions of other displaced people in their wake.
There is a close connection between internal displacement and cities under siege. Here is the UN’s estimate of the displaced population in December 2016:
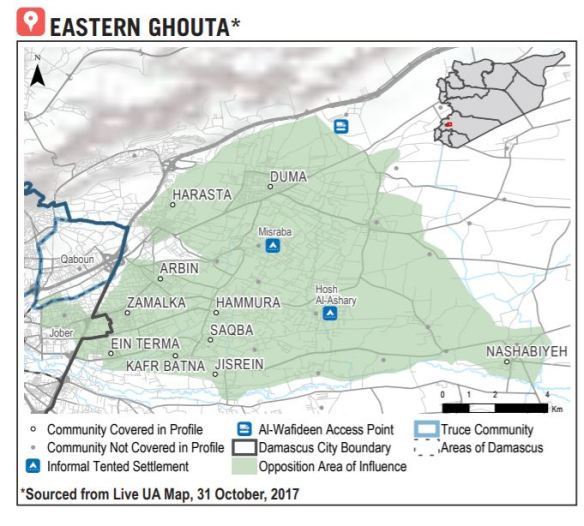
They are concentrated in towns and cities. Many people have managed to escape areas under siege, risking their lives to do so, but many others have sought refuge in towns and cities that have themselves come under siege. Here, for example, is Siege Watch‘s description of Eastern Ghouta in mid-2016:
The capture of besieged towns on the south and eastern sides of Eastern Ghouta had a negative impact on conditions throughout the entire besieged region. IDPs from the frontline areas fled into host communities that have also been subjected to the same long-term siege and lack the infrastructure and resources to support the newly displaced families. There is now a higher concentration of people living in temporary shelters or sleeping on the streets.
The UN defines a besieged area as ‘an area surrounded by armed actors with the sustained effect that humanitarian assistance cannot regularly enter, and civilians, the sick and wounded cannot regularly exit the area.’
But the definition and its application turn out to be as problematic as perhaps you would expect. Here is Annie Sparrow:
Estimates of the number of Syrians currently living under siege vary widely, according to who is doing the reporting. For example, last December [2015], the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) in Damascus communicated back to the UN secretary-general’s office that 393,700 civilians were besieged. For the same period, Siege Watch estimated that the real figure was more than one million…
From its base at the five-star Four Seasons Hotel in Damascus, OCHA decided that an area is merely “hard to reach” rather than besieged if it has received an aid convoy in the last three months, regardless of whether the supplies are sufficient for one month, let alone three.
One doesn’t need to travel far from Damascus to see how little a distinction there often is between a “hard to reach” and a “besieged” area.
I’ll return to that last, vital point, but here are two of those OCHA maps. The first shows the situation in January 2016 and the second in April 2017:
Even those attenuated maps are alarming enough, but the Syrian American Medical Society (SAMS) also believes that the OCHA reports systematically under-report the magnitude of the crisis, and in Slow Death: Life and Dearth in Syrian communities under siege (March 2015) they provided a more sensitive three-tier classification.
These are, of course, heterogeneous communities – none of the reports I have cited (nor those I will draw on later) conceals the presence of armed groups of various stripes within them, often jostling for control – but siege warfare renders them as homogeneous. The presence of civilians, for the most part desperately struggling to survive in the midst of chaos and conflict, is erased; this begins as a discursive strategy but rapidly becomes a visceral reality. In short, siege warfare becomes a version of enemy-centric counterinsurgency and counterterrorism, the Syrian government less invested in ‘performing the state’ through the provision of services than in denying services to the entire population in these areas. By these means the Assad regime has pursued a strategy that mimics the Islamic State’s determination to ‘extinguish the grey zone‘:
Like Annie, I have been impressed by the work of Siege Watch and so I’ll start with their regular reports that have provided a series of powerful insights into the effects of sieges on everyday life. In their first report they identified characteristics shared by all communities besieged by the Syrian government. When that report was compiled almost 50 communities were besieged; only two of them were under siege by forces other than the Syrian government and a third was besieged on one side by the Syrian government and on the other by Islamic State.
There are three characteristics that I want to emphasise:
Deprivation:
- ‘Civilians in the besieged areas struggle to survive. Electricity and running water are usually cut off, and there is limited (if any) access to food, fuel, and medical care. In many of these areas, civilians have died from malnutrition due to the severity with which the blockades are enforced. In all of these areas, civilians with diseases, chronic conditions, and injuries have died as a result of the lack of access to medical care. Other recorded causes of siege-related deaths include hypothermia due to the lack of heating oil in the winter, and poisoning after eating something toxic while scavenging for food. Poor sanitation conditions in the besieged areas have resulted in frequent outbreaks of infectious diseases.’
Extortion and economic development:
- ‘The pre-war economies in all of the government-besieged areas have collapsed. They have been replaced with siege economies that depend on smuggling, bribery, and local production; and because they are nearly-closed economic systems they experience extreme price volatility. Unemployment levels in besieged areas are high, reaching 100% in some of the worst Tier 1 communities such as Jobar. The Syrian government profits off of the sieges by allowing a few pro-government traders to sell goods – sometimes expired – through the checkpoints at tremendously inflated prices and taking a cut of the profits. Sometimes civilians can pay extremely high bribes to government forces or smugglers to escape the besieged areas, although both methods entail tremendous personal risk. These extortive practices have drained the areas under long-term siege of their financial resources.’
Violence:
- ‘Most of these besieged areas are targeted with violent attacks by the Syrian armed forces and its allies. In addition to sniping and the use of explosive weapons with wide area effects in populated areas, there have also been confirmed uses of internationally banned weapons such as landmines, cluster munitions, and chemical weapons…. Most of the communities also contain AOGs [Armed Opposition Groups] which defend the the areas against incursion by pro-government forces, launch offensive attacks against the Syrian military and its allies, and coordinate with the Local Councils to varying degrees. Many Siege Watch survey respondents noted that AOGs were present only around the periphery of their communities, and a few respondents from towns in the interior of the Eastern Ghouta said that AOGs were not active in their areas at all.… [In addition] both Syrian government forces and extremists compete to recruit recruit men and boys from besieged communities using threats, blackmail, fear, propaganda, and indoctrination.’
Siege Watch notes how, in consequence, ordinary people have ‘adjusted’ to these new, bleak realities: ‘Creative survival tactics such as rooftop gardening [below: eastern Aleppo], burning plastic to extract oil derivatives, and the local production of some basic medical supplies have become more common over time, and people have begun to acclimatise to a more primitive lifestyle’ [see also here].
That sentence gestures towards a sharper point made by José Ciro Martinez and Brent Eng (‘Struggling to perform the state: the politics of bread in the Syrian civil war’, International political sociology 11 (2) (2017) 130-47):
‘Most accounts [of the war in Syria] choose to privilege bellicose affairs over the humdrum concerns of daily life, which are deemed humanitarian issues separate from the violent battles and geopolitical struggles said to comprise the “actual” politics of war. This portrayal of conflict is illusory: it disregards the majority of interactions that shape both life and politics in contemporary war zones, where “most people most of the time are interacting in non-violent ways” (Tilly 2003, 12). One result of prevalent depictions of civil war is that civilians are frequently rendered powerless. If they do appear, it is as pawns in a conflict fought by armed groups autonomous from the societies they struggle to control.’
That’s an important qualification, but it plainly doesn’t erase the struggles of civilians either – which makes ‘acclimatisation’ a remarkably weak term to describe the multiple, extraordinary ways in which civilians have been forced to adjust to a new, terrifyingly abnormal ‘normal’ in order to survive. Here, for example, is a doctor in Homs describing ‘Siege Medicine’ [more here]: The Center for Civilians in Conflict has also provided a report on civilian survival strategies that lists a series of other extraordinary, collective measures (and the title, Waiting for No One, says it all). These strategies include the provision of makeshift early warning systems against incoming air attacks (spotter networks, radios and sirens); the provision and protection of medical infrastructure (in part through improvised field hospitals and the construction of underground hospitals); and the development of local aid and rescue teams (including the Syrian Civil Defence or White Helmets); protection from unexploded ordnance (‘the armed groups typically harvest them for their own makeshift weapons’ but the White Helmets and other groups have sought to render them harmless).
The Center for Civilians in Conflict has also provided a report on civilian survival strategies that lists a series of other extraordinary, collective measures (and the title, Waiting for No One, says it all). These strategies include the provision of makeshift early warning systems against incoming air attacks (spotter networks, radios and sirens); the provision and protection of medical infrastructure (in part through improvised field hospitals and the construction of underground hospitals); and the development of local aid and rescue teams (including the Syrian Civil Defence or White Helmets); protection from unexploded ordnance (‘the armed groups typically harvest them for their own makeshift weapons’ but the White Helmets and other groups have sought to render them harmless).
But Siege Watch – and José and Brent – have in mind something more: something in addition to strategies that are necessarily but none the less intimately related to direct, explosive and often catastrophic violence. They also want to emphasise the ways in which otherwise ordinary, everyday activities have been compromised and ultimately transformed by siege warfare.
Here I focus on food (in)security. Here is Annia Ciezadlo reporting from Yarmouk in Damascus:
In a dark kitchen, by the flickering light of a single safety candle, two men bundled in hats and jackets against the cold put on an impromptu video satire: live from Yarmouk, at the southernmost edge of Damascus, a cooking show for people under siege.
“This is the new dish in the camp of Yarmouk. It hasn’t even hit the market yet,” said the man on the right, 40-year-old Firas Naji, the blunt and humorous host.
He picked up a foot-long paddle of sobara, Arabic for prickly pear cactus. Holding it carefully by one end to avoid thorns, he displayed first one side and then the other for the camera.
“In the U.S., they get Kentucky [Fried Chicken], hot dogs. In Italy, spaghetti and pizza,” he said, his raspy voice caressing the names of unattainable foods. “Here in Yarmouk, we get sobara.”
“It’s not enough we have checkpoints in the streets and shelling,” he added, laying the cactus back on the counter with a sad laugh. “Even our cooking has thorns.”
Yarmouk was established in 1957 as a refugee camp for Palestinians but gradually it had absorbed more and more Syrians displaced by drought, famine and eventually fighting. As the war intensified, so the siege tightened:
The government checkpoints in and out of Yarmouk would close for four days, then five, then six. Soldiers would confiscate any amount of food over a kilo…. On July 21, 2013, the regime closed the main checkpoint into Yarmouk for good. The siege was total: Nobody could leave, and nothing could enter except what the soldiers permitted.
Over the next six months, the price of everything went up. A single radish reached $1.50 at one point; a kilo of rice was $100.
And so the inhabitants turned to gardening:
Between buildings, in abandoned lots and on rooftops, the siege gardeners of Yarmouk have been cultivating everything from eggplants to mulukhiyeh, a jute plant whose glossy leaves make a rich green stew. Come harvest time, they bag the produce into 1-kilo portions, hang the bags on the handlebars of beat-up bicycles and pedal around the camp distributing the food to their neighbors. They focus on those most in danger of starving: children, poor people and the elderly.
But the situation was much bleaker than the picture conjured up by that paragraph; the siege waxed and waned, and UNRWA was occasionally granted permission to deliver emergency relief, but the image below – of residents queuing for food supplies – shows how desperate the situation became.
Here is a woman in September 2014 describing the horrors of the siege to Jonathan Steele:
There was no anger or hysteria in her voice, just a calm recollection of facts. “You couldn’t buy bread. At the worst point a kilo of rice cost 12,000 Syrian pounds (£41), now it is 800 pounds (£2.75) compared to 100 Syrian pounds (34p) in central Damascus. It was 900 pounds (£3.10) for a kilo of tomatoes, compared to 100 here,” Reem recalled. “We had some stocks but when they gave out we used to eat wild plants. We picked and cooked them. In every family there was hepatitis because of a lack of sugar. The water was dirty. People had fevers. Your joints and bones felt stiff. My middle daughter had brucellosis and there was no medication,” she said. In October 2013, in a sign of how bad things had become, the imam of Yarmouk’s largest mosque issued a fatwa that permitted people to eat cats, dogs and donkeys.
Control of Yarmouk see-sawed between the Syrian Arab Army, Al-Nusrah and Islamic State, with thousands of civilians trapped behind the siege lines so that time and time again the community was thrown back on its own, desperately strained resources to survive.
Here is how Mamoon Yalabasi described a second satirical video from Yarmouk, made shortly after IS over-ran the camp, in April 2015:
“We are in the Yarmouk camp, the camp of plentifulness… Take a look at the floor,” said the man as the camera shows water in the street. “This is not water. This is an excess of cooking [flooding the streets].”
The youth then moved on to mockingly give his viewers advice on how to lose weight.
“Would you like to lose weight? Green tea won’t work, nor will ginger … just come to Yarmouk camp for five months, in each month you’ll lose 9kg,” he said, adding the Arabic proverb: “Ask someone with experience instead of asking a doctor.” … “We ask the troublesome channels that claim Yarmouk camp is under siege to stop reporting that. It is ‘absolutely’ [said in English] not true,” one said. “It’s true that my grandmother died of hunger but not because the camp was under siege but because my grandfather was so stingy – he never allowed her near the fridge,” he added.
Perhaps you think all this extreme, even exceptional, comforted by those images of rooftop gardens, and believe that those who bravely tended them could somehow perform their own green revolution. So here are Zeinat Akhras and her brother describing how they survived during the siege of Homs:
The examples can be multiplied many times over, but in a way this last testimony is exceptional – amongst those on which I’m drawing, at any rate – because it only became available once the siege had been lifted. Those videos from Yarmouk point towards something different: the possibility of breaching siege lines through digital media.
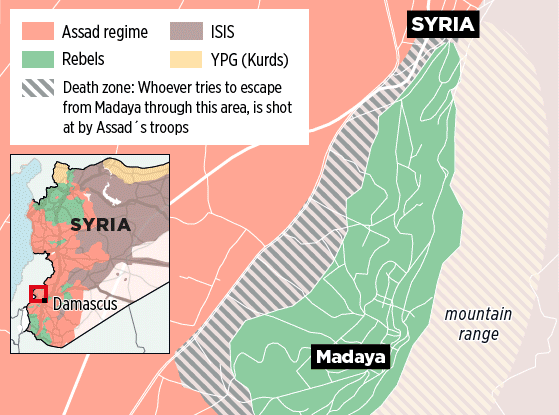
So let me turn to Madaya, a town in the Qalamoun Mountains 45 km north-west of Damascus and once famous for its fruits and vegetables. It came under siege from the Syrian Arab Army and Hezbollah militias in July 2015: the town was encircled by 65 sniper-controlled checkpoints (below) and its surrounding countryside sown with thousands of landmines.
In January 2016 the UN still classified Madaya as a ‘hard-to-reach area’, so listen to one local resident describing conditions to Amnesty International that same month:
Every day I wake up and start searching for food. I lost a lot of weight, I look like a skeleton covered only in skin. Every day, I feel that I will faint and not wake up again… I have a wife and three children. We eat once every two days to make sure that whatever we buy doesn’t run out. On other days, we have water and salt and sometimes the leaves from trees. Sometimes organizations distribute food they have bought from suppliers, but they cannot cover the needs of all the people.
In Madaya, you see walking skeletons. The children are always crying. We have many people with chronic diseases. Some told me that they go every day to the checkpoints, asking to leave, but the government won’t allow them out. We have only one field hospital, just one room, but they don’t have any medical equipment or supplies.
I’ve described that field hospital before, but Mohammad‘s testimony reminds us that war produces not only catastrophic injuries; it also produces and intensifies chronic illnesses that a protracted siege eventually renders untreatable. (The Syrian American Medical Society issued a report, Madaya: Starvation under Siege, which you can read here).
Two days later there were reports of a different digital satire: one that denied the existence of a siege in Madaya and mocked its victims.
A hashtag has swept Facebook and Twitter, #متضامن_مع_حصار_مضايا , which translates to “in solidarity with the siege on Madaya”, where individuals have posted pictures of food or skeletons, mocking those in Madaya. While many believe that the siege is a myth, some appear to be genuinely mocking the suffering of innocent people…’
The posts were subsequently removed, but here is one I captured:
Fortunately a different digital economy was already at work. Rym Momtaz, a producer with ABC News, had started a text exchange with a young mother of five children in Madaya:
We communicate through secure messaging apps over the phones, over the internet really. So the way we went about finding her was to go through a wide network of sources that we’ve cultivated over the years of covering the war in Syria. We had to work for a few weeks, I have to say, to identify the right person and then to get in touch with her and to gain her trust in order for her to feel comfortable enough to engage in this conversation with us because she felt and her family felt that it might put her in danger.
‘‘She would text me from the moment she woke up, which was very, very, early, like 5 a.m.,’ Rym explained, ‘and then she would text me truly throughout the day.’ And that same month – January 2016 – ABC started publishing those precious despatches from Madaya. ‘They can’t get out of Madaya – and we can’t get in,’ ABC News’ Foreign Editor emphasised, but ‘they can tell their story to the world.’
Working with Marvel Comics, ABC transformed her story into a free digital comic: Madaya Mom.
For Dalibor Talajic, the Marvel Comics illustrator who worked on the project,
The most striking parts is for me the most intimate ones as she – for instance, she decides to even though they are – they’re all starving, she decides to stop eating herself because this little amounts of supplies and food that she has, she distributes it to her children and of course husband. And she herself just stopped eating. And it’s not like a dramatic decision. It’s, like, a logical thing to do. These are the moments that stick with me most.
And it is through the assault on the intimacies of everyday life – on something as vital as feeding one’s family – that siege warfare is at its most vicious.
In case you are wondering how the family managed to charge their phones, not at all incidentally, here is the answer:
After protracted negotiations aid convoys were allowed in from time to time, but the situation remained grave. An aid worker who accompanied a UNICEF convoy into Madaya in September 2016 described the stories told by patients who flocked to a makeshift medical clinic:
Parents whose children had stopped eating because their bodies could no longer tolerate only rice and beans. Children who could no longer walk straight because of the lack of Vitamin D and micronutrients that had riddled their bones with rickets, or who had stopped growing entirely, stunted from lack of essential vitamins. One mother showed us her baby’s bottle filled with rice water – the teat so worn it had to be sewn back to together. “Look at what I am feeding my child” she said.
Almost everyone we spoke to asked for protein – meat, eggs, milk, vegetables – something more to sustain themselves than the dry goods that were available. One mother explained that every time her child now smells boiled burgal, she starts to cry.
The doctor reported an increase in miscarriages, 10 cases in the last 6 months, because of the nutritional status of mothers. Over the last year alone, he has had to perform over 60 caesarian sections. This number was unheard of before the crisis, she told us But women no longer have the strength for childbirth, and many pregnancies go over term, again because of the poor health of pregnant women.
Six months later life in Madaya remained precarious in the extreme:
 Throughout the siege there were accusations of profiteering, but these ran in both directions (it is partly through them that Hezbollah elected to acknowledge the suffering of the city – only to point the fingers of blame at the rebels inside). According to Avi Asher-Schapiro for VICE News, who spoke to the local leader of Ahrar al-Sham, Abdulrahman, via Skype in January 2016:
Throughout the siege there were accusations of profiteering, but these ran in both directions (it is partly through them that Hezbollah elected to acknowledge the suffering of the city – only to point the fingers of blame at the rebels inside). According to Avi Asher-Schapiro for VICE News, who spoke to the local leader of Ahrar al-Sham, Abdulrahman, via Skype in January 2016:
Hezbollah media outlets are accusing Abudlrahman and his men of confiscating food in Madaya, holding the population hostage, and profiteering during the crisis. In early January, a video surfaced of a woman from Madaya condemning rebels for hoarding food among themselves. The rebels are “only traders in people’s blood,” she told a scrum of reporters who gathered at the barricades outside Madaya. “They only care about securing food supplies for their families.”
That video [above] was aired around the world by Reuters and Al Jazeera. The accusations enraged Abdulrahman. “When Madaya goes hungry, we go hungry,” he says. “These are vicious lies.” VICE News spoke with another woman who claimed to be at the barricades that day. Although it was impossible to verify her claims, she said that Hezbollah fighters — who can be seen in the video frame — told women to condemn the rebels and praise Assad in exchange for food and safe passage from the town.
In a press release from early January, Hezbollah also accused Abdulrahman of profiteering. “Armed groups in Madaya control food supplies within the town and sell to whoever can afford it,” the statement read, “Thus, starvation is widespread among poor civilians.” VICE News spoke to a Hezbollah commander stationed outside Madaya who repeated these claims, and said that Hezbollah has been sending food inside the town. The rebels, he said, are keeping it for themselves. He also strongly denied that Hezbollah was trading food for propaganda.
VICE News also spoke with aid workers at the Doctors Without Borders-affiliated field hospital in Madaya, who reported no interference from Abdulrahman’s men in the dispensation of aid.
For further, still more shocking twists on the story, see here and a response here. It’s difficult to adjudicate these competing claims in the face of skilfully organised propaganda campaigns (in which the alt.left is often as grotesque as the alt.right), but wherever the truth lies, it is clear that food has been consistently transformed into a weapon of war (‘surrender or starve‘) – a crime expressly forbidden by international humanitarian law (see also here) – and that 40,000 civilians inside Madaya were trapped in the midst of the battle.
In my previous post on this subject, I described all this as the back-story to the carnage now taking place in Idlib, in eastern Ghouta and elsewhere, but it is of course only one back-story: there are many more. Still, on 14 April 2017 under the ‘Four Towns Agreement’ a fleet of sixty buses transported several thousand people, rebels and civilians, from Madaya – to Idlib.
Only 2,200 out of 40,000 people signed up to go, and ‘Madaya Mom’ expressed the catch-22 facing the besieged population perfectly:
If we leave, we’re labeled terrorists and we go to Idlib where the chemical attack happened last week; and if we stay we don’t know how the government will treat us.
At first, those who left were relieved and even heartened. Deutsche Welle spoke with one young evacuee from Madaya soon after he arrived in Idlib:
I was surprised. I saw markets [below, June 2017], people walking in the streets; there is electricity, internet, ice cream and food – things we did not have in Madaya. Madaya and Zabadani are destroyed. In Idlib, the destruction is not too bad. There are a lot of cars and I was really surprised to see cars. I felt like the little children that came from Madaya to Idlib: they were surprised when they saw a banana, a cherry, biscuits or chocolate. They have never seen that before. It sounds stupid, but I felt a little bit the same when I saw cars again.
I can eat everything. The first thing I ate was fried chicken and it was great. And I have had a lot of chocolate, too.
But as the interview progressed, his elation was punctured by a growing realisation of the bleak future ahead:
But in general, Idlib is a poor city… I started to search for jobs, but there are almost no jobs here. Idlib is like a big prison. It’s like Gaza. It’s like Madaya, but a big Madaya. So we are imprisoned here.
We know what horrors lay in wait, and we know something of what is happening in Idlib now. But what of Madaya? Here are extracts from a report (‘community profile’) for September 2017 (you can find more from SIRF/REACH here):
- Movement was unrestricted within Madaya. For movement in and out of the area, two access points have been used since the implementation of the Four Towns Agreement. In September, 26-50% of the population were reportedly able to use formal access points providing they showed identi cation. However, men reportedly did not feel safe using the access points, fearing conscription and detention when crossing, while both men and women reported verbal harassment.
- Since May 2017, commercial vehicle access has been permitted to the area. However, access restrictions on vehicle entry continued to be reported in September and included documentation requirements, confiscation of loads, required fees and limited entry depending on the day or time.
- Humanitarian vehicle entry has reportedly not been permitted for the past six months.
- The cost of a standard food basket in Madaya has remained stable since May 2017, with the average cost around 12% more expensive than nearby communities not classi ed as besieged or hard-to-reach.
- Water continued to be insufficient and some residents reportedly reallocated money intended for other things to purchase water. Meanwhile, access to generators remained stable at 4-8 hours a day in all areas of the community.
I’m conscious of how much I haven’t been able to address in this post. In particular, I’ve chosen to focus on the ‘silent violence’ of hunger and malnutrition rather than the explosive violence of mortars, missiles and bombs. The two coincide in all sorts of ways – think, for example, of the air strikes on bakeries, what Anna Ciezadlo called ‘the war on bread‘, and on hospitals and clinics – but the contrast is really my point. As one resident of Aleppo told Amnesty,
You need months before you die of starvation. The air strike attacks were a different story. You could die from a piece of shrapnel in a fraction of a second. Nobody was protected from the air strikes and shelling. Civilians, rebels, buildings, cars, bridges, trees, gardens etc. were all a target.
And so one final digital satire. In April 2016 the Syrian government held elections and claimed that even opposition-held areas were enthusiastically participating. Responding to what they called ‘the theatrics of the Assad regime’, teenagers in Madaya posted a video of their own mock hustings: The rival candidates were “Deadly Starvation”, “Deadly Illness”, and “Airstrikes”.
The rival candidates were “Deadly Starvation”, “Deadly Illness”, and “Airstrikes”.