One of the most shop-soiled phrases of the past several weeks and months is “boots on the ground” (or the lack of them). You can find historical and contemporary discussions from the US military here and here, but the most recent – and recurrent – instance is President Obama’s insistence that, whatever else the United States will do in Iraq and Syria to counter the aggressive advance of the Islamic State, it won’t involve “boots on the ground”. The reasons are not difficult to discern, and they involve the substitution of “boots on the ground” for “bodies in bags” (on which, see the American Friends Service Committee exhibition, “Eyes Wide Open“: also the Burning Man version here).
But they also involve an extraordinary (but, again, by no means unprecedented) restriction of what constitutes armed combat. Mark Landler has a very good discussion of this in the New York Times:
American advisers could be sent to the front lines alongside Iraqi and Kurdish troops, and could even call in airstrikes, without directly engaging the enemy. It is a definition rejected by virtually every military expert.
“Calling in airstrikes is just as much combat as firing a rifle at someone,” said John A. Nagl, a retired lieutenant colonel who served in a tank battalion in Iraq and helped write the Army’s counterinsurgency field manual. “What that guy really is doing is painting a house with a laser designator that results in that house being vaporized.”
The American advisers are armed, and if they are shot at by the enemy, they are authorized to return fire. In a close combat advisory role in a city, experts said, the American troops would tell Iraqi commanders which house to hit, how much ammunition to use in an assault, and how to organize medical evacuation for their troops…
“If you’re trying to deploy a military effect on the ground, you’re in combat,” said Paul D. Eaton, a retired Army general who helped train Iraqi troops and is now an adviser to the National Security Network. “You may not be in direct combat, but it’s a combat mission.”
There are also not very muffled echoes of Vietnam and the US Military Assistance Command.
This is very much on my mind, because I’ve been busy finishing the long-form version of “The Natures of War”, and in the process radically re-working my discussion of the ground war in Vietnam. This has given me a new insight into what “boots on the ground” means – with an emphasis on the “ground”, or what my good friend Gastón Gordillo prefers to call terrain – and here is an extract (I’ll post the full draft next week, which will include the references and the footnotes).
***

Then as now the scale of support involved in combat operations meant that many soldiers never left their bases – in Vietnam the ratio of support to combat troops was roughly 10 to 1 [this is the ratio cited by most historians, but the US Army prefers a much lower “Tooth to Tail” ratio: see here] – but those that did had to carry their world on their backs. On a long patrol they might be resupplied by helicopter, but that could never be guaranteed. In addition to a rifle, most men carried at least 60 pounds: multiple quart canteens of water (at least two and sometimes as many as eight: ‘There is never, ever enough water’) and canned C-rations; ammunition and grenades; and a poncho or half-shelter which doubled as a stretcher or a shroud if they were hit. In addition, radio operators carried a PRC-25 field radio, which weighed 23 pounds, and spare batteries, while mortar crews lugged a firing tube and base plate weighing around 40 pounds, and their bearers carried four mortar rounds (which added 32 pounds of dead weight to their load). This mattered because, as one newly arrived lieutenant soon realised, ‘the jungle would exact a toll for every ounce I carried.’ ‘We dumped everything we didn’t absolutely need,’ one GI explained, but still the rucksack frame and webbing rubbed and cut so ‘our waists and shoulders were covered with “saddle sores” that were kept raw by sweat and dirt and cartridge belts and packs.’ Everyone, he said ‘was in a constant world of hurt.’
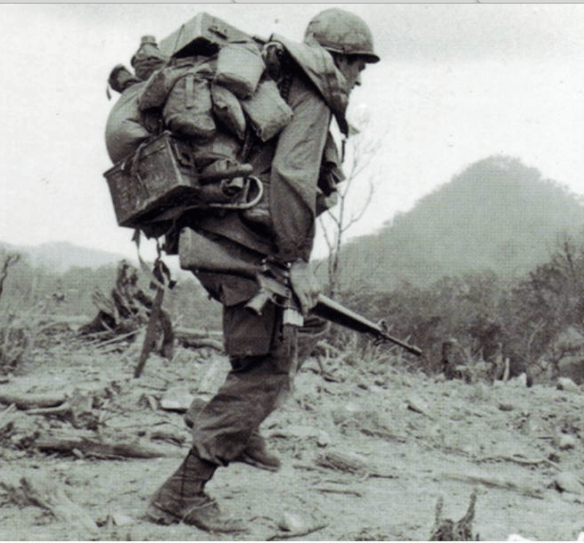

It was just as tough on the legs. Tim O’Brien translates the equipment list – ‘the things they carried’ – into its impact on the lower body:
‘We walked along. Forward with the left leg, plant the foot, lock the knee, arch the ankle. Push the leg into the paddy, stiffen the spine. Let the war rest there atop the left leg: the rucksack, the radio, the hand grenades, the magazines of golden ammo, the rifle, the steel helmet, the jingling dog-tags, the body’s own fat and water and meat, the whole contingent of warring artefacts and flesh. Let it all perch there, rocking on top of the left leg, fastened and tied and anchored by latches and zippers and snaps and nylon cord. Packhorse for the soul.’

O’Brien was describing a patrol moving through rice paddies, and these imposed their own burdens on soldiers. Out in the open they were vulnerable to attack or sniper fire, and they avoided the dikes which were often mined or booby-trapped.
‘Instead, we struggled through the sucking mud of the paddies. The banks of the streams were especially treacherous. Each step through the soft muck was torture, and every few steps a man would sink in mud up to his crotch. The gnarled roots of the mangroves could twist an ankle or a knee in a second. The putrid stench of rotting vegetation permeated the stifling humid air, and canteens were emptied quickly.’
‘The water in these pestilential miasmas was stagnant, muddy and fetid,’ explained one lieutenant, ‘with all kinds of flotsam, including mosquito larvae and water buffalo faeces applied as fertiliser’. Beneath the murky water lurked the menace of punji stakes made of split bamboo that could pierce a boot and put a soldier out of action; worse, the wound could become infected from the dung-laden water, and air evacuation was often imperative. Then there were the leeches: ‘When we reached the other side of the rice paddies,’ the lieutenant continued, ‘my men dropped their pants and burned the already engorged leeches off their ankles and penises with lit cigarettes; even the non-smokers carried cigarettes for this purpose.’
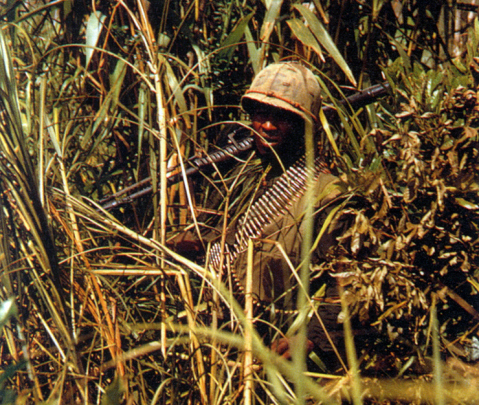

In the Central Highlands soldiers had to fight their way through triple-canopied jungle and up thickly forested mountain sides. Like their comrades in the paddy-fields, they learned to avoid the beaten track. They rarely used trails, which were notorious for mines and booby-traps that, as Philip Caputo explained, turned ‘an infantryman’s world upside down’:
‘The foot soldier has a special feeling for the ground. He walks on it, fights on it, sleeps and eats on it; the ground shelters him under fire; he digs his home in it. But mines and booby traps transform that friendly, familiar earth into a thing of menace, a thing to be feared as much as machine guns or mortar shells. The infantryman knows that any moment the ground he is walking on can erupt and kill him; kill him if he’s lucky. If he’s unlucky, he will be turned into a blind, deaf, emasculated, legless shell.’
He might have been talking about the cyborg natures of the Western Front or the Western Desert, but in Vietnam’s guerrilla war there were few fixed minefields beyond the Demilitarized Zone. Base perimeters were systematically mined by the US and its allies, and the North Vietnamese often mined clearings that could be used as helicopter landing zones. But it was the transience of mining by the North Vietnamese Army and the Viet Cong – its improvisational, opportunistic nature – that was so threatening. ‘The NVA were so good at moving mines around that they would put the minefield out at dusk along a patrol route and take it in before dawn’ so that ‘you could clear one area and there would be mines there the next night.’ Booby-traps could be anywhere: ‘They hang from trees. They nestle in shrubbery. They lie under the sand.’ Denied the trails, soldiers had to hack a path with their machetes or Ka-Bars or more often, to muffle the sound of their painfully slow progress, they threaded their way between the trees and the choking vines:
‘Up ridges, down ridges, over ridges, wading through rocky streams, hacking at jungle growth, breathing in and hopefully breathing out some of the constant bugs that continuously swarmed around our heads, watching our skin as it quickly deteriorated from the numerous bites, scrapes, cuts, tears, thorns, and other abuses of the environment that attempted to beat our bodies into submission. The clothes and boots forming the inanimate part of our body protection were quickly drenched with sweat, dirt, mashed bugs, and the mixed blood and juices from both the bugs’ bodies and our own.’
In the Highlands they encountered other cyborg natures. Devastating Arc Light strikes by B-52 bombers produced a surreal, cratered moonscape whose blasted terrain was even more difficult to negotiate than pristine rainforest:
‘The jungle had been torn to smithereens by the big bombs. Trees had been ripped from the ground forming an abatis of twisted, interattached splintered branches, vines, and roots that was more impenetrable than the worst the natural jungle had to offer.’

The craters would be ‘littered with huge pieces of bomb shrapnel’ and unexploded bombs that had not burrowed into the soft earth: their ‘green shapes that protrude menacingly from the red dirt add yet another facet of terror for us to deal with.’ It was impossible to avoid the deep craters: ‘They are too congested; the muddy holes sap our strength as we slide down into their depths, wade through the stagnant green rainwater and then climb fifteen feet up to the slope to the opposite rim.’ If the bombs had found their target then the patrols faced more than a physical barrier, because the bomb field would also contain decomposed corpses, animal and human, and body parts. Delezen continued:
‘[T]he heavy smell of death is around us and is growing stronger as we move. Soon I discover that the source of the overpowering stench is a shallow bomb crater positioned along our path; the crater was probably gouged into the earth by a five hundred pound bomb. There is a naked leg sticking out of the dark hole; on the foot is a rubber sandal made from a discarded truck tire. It looks as though the crater is moving … the movement is rats. In the dusk it looks like a blackish gray carpet covering the mangled, bloated bodies that the grunts have thrown into the hole. The bottom of the hole is full of large maggots that create the illusion that the crater is shimmering. I determine that there are at least twelve enemy bodies that lay intertwined in the crater. The huge rats are snapping at each other as they feed on the dead soldiers; this has to be the entrance to hell itself. The smell is overwhelming; it is so strong that I can taste it.’
B-52s and long-range artillery were not the only means of ravaging the land. It was also impregnated with the residues of napalm and other chemical toxins, and long after an air strike these could still irritate your eyes, make you gag and burn your skin. They also turned any vertical movement into a dangerous glissade:
‘[T]he mountain that we are now climbing has been attacked by countless sorties of Phantom jets delivering “snake and nape.” The splintered, tortured tree trunks are black and charred from the napalm and the oily gel that did not ignite has mixed with the red mud, turning it into a texture similar to axle grease. My pack and ammo belt are waterlogged and have picked up extra weight from the greasy mud.
‘The mud has clogged the lug soles of our jungle boots and it is difficult not to slip; we know that if we lose our footing we will end up at the bottom of the mountain. I use my weapon to climb, digging the stock into the mud as a brace while I grab the next bomb-blasted tree trunk. The oily napalm has lubricated the entire mountain, it has soaked into the burned trees; we have to grasp each splintered trunk in a hug. The black M-16 no longer resembles a rifle; it is encased within a shapeless red blob of sticky mud. After a while, I have to use my Ka-Bar to climb with. I stab the earth ahead and then pull myself up; the deep, soft mud soon renders this effort useless.’
***
There’s much, much more, as the full post will show, but I’ve said enough to convey some of the ways in which “boots on the ground” are involved in my developing interest in corpography and war. This extract also raises two other issues that I can’t develop in any detail in the essay.
 The first turns on the parallel experience of the National Liberation Front [the ‘Viet Cong”] and the North Vietnamese Army. The Americans assumed that their enemies were creatures of the jungle (in more ways than one), but many of them were recruited from towns and cities and had little or no experience of the rainforest and no idea of the privations that jungle warfare would impose on them. This is made clear in Truon Nhu Tang‘s A Viet Cong memoir, which is widely cited, but the best and most directly relevant account that I know is the truly remarkable collaboration between John Edmund Delezen and Nguyen Van Tuan, Red Plateau, which describes a North Vietnamese battalion ‘comprised of boys from towns and farms and most knew very little about the forest-enshrouded mountains’. I cite Delezen in the extract above – his Eye of the tiger is one of the very best personal accounts I’ve read – but his collaboration with his erstwhile enemy is just as compelling. Here is Nguyen Van Tuan’s inventory of the things carried by the NVA:
The first turns on the parallel experience of the National Liberation Front [the ‘Viet Cong”] and the North Vietnamese Army. The Americans assumed that their enemies were creatures of the jungle (in more ways than one), but many of them were recruited from towns and cities and had little or no experience of the rainforest and no idea of the privations that jungle warfare would impose on them. This is made clear in Truon Nhu Tang‘s A Viet Cong memoir, which is widely cited, but the best and most directly relevant account that I know is the truly remarkable collaboration between John Edmund Delezen and Nguyen Van Tuan, Red Plateau, which describes a North Vietnamese battalion ‘comprised of boys from towns and farms and most knew very little about the forest-enshrouded mountains’. I cite Delezen in the extract above – his Eye of the tiger is one of the very best personal accounts I’ve read – but his collaboration with his erstwhile enemy is just as compelling. Here is Nguyen Van Tuan’s inventory of the things carried by the NVA:
‘As dark nears we once again move onto the path and begin our trek south, I curse my pack; if not for this burden I would move effortlessly. Each pack contains an extra uniform and one pair of pajamas, a rain-sheet, a ground cloth, a shovel, ammunition, grenades, explosives, a small medical kit, B-40 rockets for the RPG crews or boxes of machine gun ammunition for the crews and toilet articles which are for the most part extremely minimal. In addition to this loaded pack, we each carry our individual weapon with ammunition vest, knife and canteen of water. The heavy weapon crews and mortar teams suffer worse…much worse, the load they carry is unimaginable….
‘When we pause to fill canteens from a stream, we try to rearrange the loads we are burdened with; it is a futile task, there is no relief, each arrangement brings its own torment. The loads we bear begin to increase as the supplies carried by those who fall prey to fever and those who carry the litters must be redistributed; our packs remain things that we continue to curse.’
The second issue is the genealogy of “the things they carried”, and Tom Atkinson (really; not quite “Tommy Atkins” but close enough) has provided an extremely interesting visual reconstruction of what he calls “Soldiers’ Inventories” here (you can also find more here and here). His 13 images extend from the Battle of Hastings (1066) through the Somme in 1916 and the Battle of Arnhem in 1944 to Helmand in 2014 (shown below), though since this is an inventory of British soldiers there’s no trace of Vietnam. (Interestingly, though, a common complaint from US soldiers and especially Marines in Vietnam was that much of their equipment was outdated and derived from the Second World War – including, on occasion, their canned rations).

Here’s the key for a close-support sapper, Royal Engineers, Helmland Province, 2014:
1 Silva compass – used for basic navigation and fire control orders
2 Karabiner – used for securing kit and equipment to the vehicles
3 Osprey body armour shoulder and neck attachments – the armour increases protection but can be very restrictive so these parts are detachable depending on the threat assessment
4 Osprey body armour; can be fitted with pouches to carry everything from ammunition, water, first aid kits and grenade or with plates and protective attachments (as shown)
5 Notebook
6 Warm weather hat
7 Spare clothing including underwear trousers, UBAS (Under body Armour Shirt) and normal shirt
8 Dog tags
9 A desert issued belt
10 Beret – used for repatriation ceremonies, vigils and large parades
11 Shemagh – to soak up sweat and also a dust guard
12 Gloves
13 Sandals – issued kit, as soldiers may need to run for cover even while showering
14 Boots
15 Multi tool
16 Washkit
17 GSR – general service respirator
18 A housewife – a basic sewing kit; a soldier has to repair his own rips and tears on the ground
19 Socks, scarf, wristwatch
20 Camel pack – drinking water pack
21 Cooker and mug and tea making kit
22 Rations – quantity will depend on the task but soldiers normally carry about 24 hours worth
23 First aid kit including the (black) tourniquet and (grey) first field dressing
24 Ballistic protection – used to protect the groin from IED blast
25 Knee pads – offer protection to a soldier whilst “taking a knee” from the heat of the ground or rocky areas
26 Sleeping bag with an inflatable roll mat
27 Camera, cigarettes
28 Radio – BOWMAN Radio system (HF, VHF or even SAT Comms), daysack could also be fitted with ECM (Electronic counter measures)
29 Personal role radio – used for line of sight communications within a small patrol
30 Magazine
31 Envelopes
32 Mine extraction kit fitted with a mine prodder, instruction and mine marking kit
33 Weapon cleaning kit
34 Holster
35 Pistol – used as a second weapon system and in confined spaces or where a “long” weapon is unsuitable. Sig and Glock have mostly replaced the Browning 9mm calibre
36 Bar mine – anti-tank landmine
37 Head torch – can be fitted with coloured lenses for more tactical situations
38 Bayonet and bayonet scabbard
39 SA80 A2 fitted with a desert hand guard, upgraded flash eliminator and bipod, all issued for Afghanistan and a SUSAT sight system. It is 5.56 calibre and is here issued with 6 magazines which can hold 30 rounds each
40 Ballistic eye protection – normally goggles or sunglasses
41 Mk 6 Helmet fitted with Helmet mounted night vision systems
42 iPad – personal effect for down time
43 Poncho
I’ll leave the least word to Karl Marlantes, whose splendid Vietnam novel Matterhorn I’ve recommended before. This comes from his What it is like to go to war (2011), and in so many ways returns us to where I came in:
I am not saying that the infantry today has it easy. Certainly the communications with home have changed, but the field conditions, such as filth, cold, heat, fatigue, and lack of sleep, have not changed since the infantry was using rocks. However, the trend is clear. Robots are already being deployed for fighting in cities. And soon they will be able to be controlled from Nevada.
The landscape acts as an omnipresent consciousness, an apparition always in the corner of [Lieutenant] Black’s eye, and Renehan attaches to it layers of reverence and dread and unknowable quasi-mysticism; the valley is capable of anything. This infection spreads slowly for the reader, and Renehan says his writing process followed a similar path. “I more or less thought I was setting out to write a mystery story that happened to be set in a war. But as I started writing it I realized it was growing into something different in my mind, and it changed on paper too.” A detective story becomes a heroin- and concussion-fueled dreamscape that crosses genres. “Going After Cacciato gave me comfort in writing the parts of The Valley that become almost surreal,” Renehan said. “It reassured me that this sort of thing is okay, because it’s a war novel, right?”