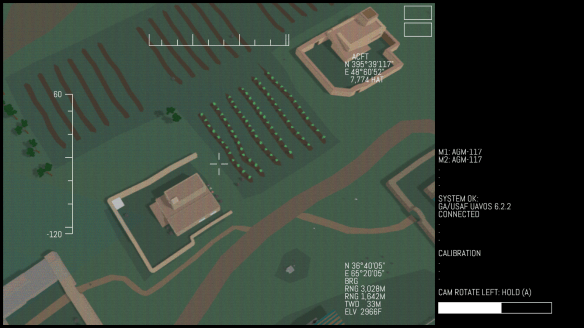
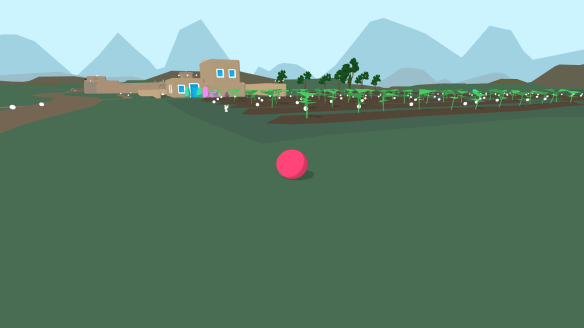
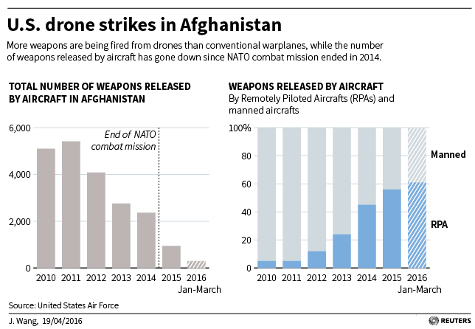
An update on Joe DeLappe‘s Killbox project (my original post, with links to more info on the concept of a killbox, is here).
Over at Quartz, Ananya Bhattacharya provides more details about the latest iteration of the simulation:
Killbox, an online two-player game named after the military term for an area targeted for destruction, serves as a critique of drone warfare. One player is a civilian exploring her surroundings with few instructions. The second player is guided with tasks, leading up to the administration of a drone strike. Even if the drone pilot player refuses to deploy the weapons, autopilot kicks in and carries out the attack. When it hits, the drone pilot can see the extent of the destruction on the ground but hear nothing. Meanwhile, the child on the ground is barraged by sound. And just in case the first strike doesn’t demolish enough, a second strike is administered—the classic “double-tap” attack to stop rescuers from getting help to the injured and retrieving the deceased.
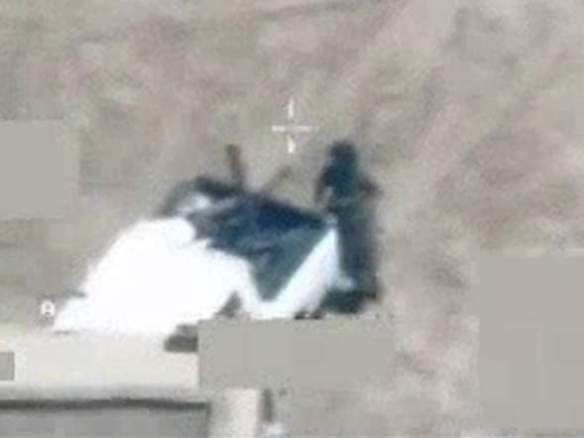
The game is modelled – in some measure, at least – on the drone strike that killed Mamana Bibi as she gathered okra from the fields around her home in North Waziristan:
The characters in the game aren’t realistic though—they look like odd-shaped blobs. At first, non-human avatars seem less effective, but there’s meaning behind the simplistic design: “We were looking at the map where the drone strike killed people and these maps identified victims with little dots,” said DeLappe. “Almost like map pins, like they’ve been symbolically degraded in some way.”
I opened my essay on drone strikes in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas – and on the constitution of the FATA as a space of exception (see “Dirty Dancing” under the DOWNLOADS tab) – with a comparison between this strike, the murder of an innocent grandmother as she worked in the fields with her grandchildren, and the targeted killing of Baitullah Mehsud, the leader of the Pakistan Taliban, in South Waziristan in 2009 (see also my posts here and here).
In Drone: remote control warfare Hugh Gusterson opens with exactly the same comparison but to a different effect – and one that resonates with Killbox. Drawing on Jane Mayer‘s account of the assassination of Mehsud, based on testimony from those who watched the video feed from the Predator, he writes:
A technology that is almost magical gives its owners, who are looking on the scene from high in the sky, a godlike power over life and death. The observation of the scene is simultaneously intimate and remote. It is also deeply asymmetrical: Mehsud, unaware of his exposure, is watched by faraway drone operators who can see him as if close up, reclining on the roof of his house on a hot evening as his wife attends to his medical needs. They get to frame the picture while he does not even realize he is in it. Without warning, he is killed as if by a god’s thunderbolt from the sky. Seen from Virginia, the drone strike is quick, clean, and bloodless. Mehsud’s death is instant. Nor, described unambiguously as a terrorist, does he seem undeserving of death. Twelve people die altogether, but the narrative marks only Mehsud’s death as significant. The other deaths are almost outside the frame. And in a way that amplifies the strange mix of distance and intimacy, the scene is mediated entirely through a single sense—vision. The attack has no sound, smell, taste, or texture. And we are invited to experience it through a narrative of mastery and control—of the cool, righteous exercise of overwhelming power.
Drawing on testimony from Mamana Bibi’s family before a virtually empty Congressional hearing, Hugh writes:
This account is from the point of view of the victims, not the executioners. We share the experience of those who do not even realize that they are in the crosshairs until they are attacked. The account emphasizes the sudden incomprehensible eruption of violent force, literally out of the blue, in a warm scene of familial togetherness on an important holy day. We are led to experience the drone strike through multiple senses, of which sight may be the least salient: we are told about the blackness of the smoke, the sound of the screaming, the smell of the explosion, the sensation of the ground trembling, and the pain of shrapnel wounds. Unlike the first account, the narrative does not end shortly after the drone strike but dwells on the aftermath—the physical pain of the survivors, the enduring grief over the loss of the person “that held our family together.” Above all, this account foregrounds what is absent in the view from CIA headquarters—the psychological suffering of those on the ground, especially children, and the sense that the safe predictability of life has been permanently destroyed. It is a narrative of helplessness, terror, and injustice. The drone operators’ perspective was remote and objectifying, but this narrative is so affecting that it made the translator break down in tears.
The special effects created by privileging the visual are explored with skill and sensitivity in Nasser Hussain‘s brilliant essay, ‘The sound of terror: phenomenology of a drone strike‘, here.
[I]n order to widen our vision, I provide a phenomenology of drone strikes, examining both how the world appears through the lens of a drone camera and the experience of the people on the ground. What is it like to watch a drone’s footage, or to wait below for it to strike? What does the drone’s camera capture, and what does it occlude?
… Although the pilots can hear ground commands, there is no microphone equivalent to the micro-scopic gaze of the drone’s camera. This mute world of dumb figures moving about on a screen has particular consequences for how we experience the image. As Michel Chion notes in The Voice in Cinema, although sound or voice is easily swallowed up by the image, it nonetheless structures the image: “only the creators of a film’s sound—recordist, sound effects person, mixer, director—know that if you alter or remove these sounds, the image is no longer the same.” In the case of the drone strike footage, the lack of synchronic sound renders it a ghostly world in which the figures seem unalive, even before they are killed. The gaze hovers above in silence. The detachment that critics of drone operations worry about comes partially from the silence of the footage.
… If drone operators can see but not hear the world below them, the exact oppositeis true for people on the ground. Because drones are able to hover at or above 30 thousand feet, they are mostly invisible to the people below them. But they can be heard. Many people from the tribal areas of Pakistan (FATA) describe the sound as a low-grade, perpetual buzzing, a signal that a strike could occur at any time. The locals call the drones machar, mosquitos. Because the drone can surveil the area for hours at a time, and because each round of surveillance may or may not result in a strike, the fear and anxiety among civilians is diffuse and chronic.
That sense of optical power is not necessarily one of detachment. For we surely know how vision, power and desire can be commingled; and today I learned – from Theodor Nadelson‘s Trained to kill: soldiers at war – that (some) US Marines describe setting their sights on a human target as ‘eye fucking’…